\(\displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^6{ }^{51-k} C_3\) is equal to
- ${ }^{51} C _3-{ }^{45} C _3$
- ${ }^{52} C _4-{ }^{45} C _4$
- ${ }^{52} C _3-{ }^{45} C _3$
- ${ }^{51} C _4-{ }^{45} C _4$
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
The given summation is:
\( \sum_{k=0}^6 \binom{51-k}{3} \)
Step 1: Rewrite the summation
This summation can be expanded as:
\( \sum_{k=0}^6 \binom{51-k}{3} = \binom{51}{3} + \binom{50}{3} + \dots + \binom{45}{3}. \)
This is a finite summation of combinations.
Step 2: Use the telescoping property of combinations
We utilize the following identity for summation of combinations:
\( \sum_{r=a}^b \binom{r}{p} = \binom{b+1}{p+1} - \binom{a}{p+1} \)
Here, let \( a=45, b=51\), and \(p=3\). Substituting these values:
\( \sum_{k=0}^6 \binom{51-k}{3} = \binom{52}{4} - \binom{45}{4}. \)
Step 3: Verify the answer
From the above calculation, we see that:
\( \sum_{k=0}^6 \binom{51-k}{3} = \binom{52}{4} - \binom{45}{4}. \)
This matches option (3).
Final Answer:
\( \boxed{\binom{52}{4} - \binom{45}{4}} \)
Approach Solution -2
Top Questions on Integration by Partial Fractions
If \[ \int (\sin x)^{-\frac{11}{2}} (\cos x)^{-\frac{5}{2}} \, dx \] is equal to \[ -\frac{p_1}{q_1}(\cot x)^{\frac{9}{2}} -\frac{p_2}{q_2}(\cot x)^{\frac{5}{2}} -\frac{p_3}{q_3}(\cot x)^{\frac{1}{2}} +\frac{p_4}{q_4}(\cot x)^{-\frac{3}{2}} + C, \] where \( p_i, q_i \) are positive integers with \( \gcd(p_i,q_i)=1 \) for \( i=1,2,3,4 \), then the value of \[ \frac{15\,p_1 p_2 p_3 p_4}{q_1 q_2 q_3 q_4} \] is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let for \( f(x) = 7\tan^8 x + 7\tan^6 x - 3\tan^4 x - 3\tan^2 x \), \( I_1 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} f(x)dx \) and \( I_2 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} x f(x)dx \). Then \( 7I_1 + 12I_2 \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let {an}n=0∞ be a sequence such that a0=a1=0 and an+2=3an+1−2an+1,∀ n≥0. Then a25a23−2a25a22−2a23a24+4a22a24 is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Find the value of \( \frac{5}{6} + \frac{3}{4} \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- If ∫ (2x + 3)/((x - 1)(x^2 + 1)) dx = log_x {(x - 1)^(5/2)(x^2 + 1)^a} - (1/2) tan^(-1)x + C, then the value of a is:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
- 10 mole of an ideal gas is undergoing the process shown in the figure. The heat involved in the process from \( P_1 \) to \( P_2 \) is \( \alpha \) Joule \((P_1 = 21.7 \text{ Pa}, P_2 = 30 \text{ Pa}, C_v = 21 \text{ J/K mol}, R = 8.3 \text{ J/mol K})\). The value of \( \alpha \) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- The system of linear equations
$x + y + z = 6$
$2x + 5y + az = 36$
$x + 2y + 3z = b$
has- JEE Main - 2026
- Matrices and Determinants
- The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with time period \(T\) is expressed as \[ x(t)=A\sin\omega t, \] where \(A\) is the amplitude of oscillation. If the maximum value of the potential energy of the oscillator is found at \[ t=\frac{T}{2\beta}, \] then the value of \(\beta\) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Waves and Oscillations
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
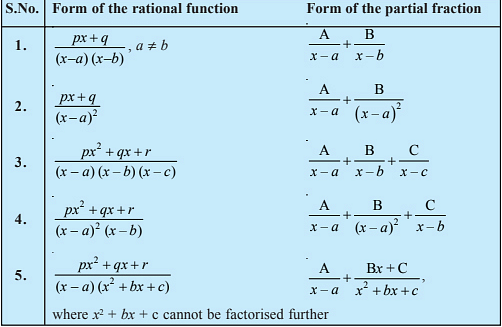
For examples,
