A monoatomic gas performs a work of \(\frac Q4\) where \(Q\) is the heat supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas will be ____ \(R\) during this transformation. Where \(R\) is the gas constant.
Correct Answer: 2
Solution and Explanation
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
\(Δ U = Δ Q -\frac {Δ Q}{4}\)
\(Δ U = \frac 34Δ Q\)
\(⇒ nC_vΔT = \frac 34nCΔT\)
\(⇒ C = \frac {4C_v}{3}\)
\(= 2R\)
So, the answer is \(2\).
Top Questions on specific heat capacity
Match List-I with List-II.
List-I List-II (A) Heat capacity of body (I) \( J\,kg^{-1} \) (B) Specific heat capacity of body (II) \( J\,K^{-1} \) (C) Latent heat (III) \( J\,kg^{-1}K^{-1} \) (D) Thermal conductivity (IV) \( J\,m^{-1}K^{-1}s^{-1} \) - JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- specific heat capacity
- Product of uncertainty in position (\(\Delta x\)) and uncertainty in velocity (\(\Delta v\)) has unit:
- KEAM - 2025
- Physics
- specific heat capacity
- If \( \frac{C_p}{C_v} \) is unity for a process, \( PV^{\gamma} = \text{constant} \), then the process is:
- KEAM - 2025
- Physics
- specific heat capacity
- Specific heat capacity of diatomic gas at constant volume:
- KEAM - 2025
- Physics
- specific heat capacity
- The circuit shown in the figure contains an inductor L, a capacitor \(C_0\), a resistor\( R_0\) and an ideal battery. The circuit also contains two keys \(K_1\) and \(K_2\). Initially, both the keys are open and there is no charge on the capacitor. At an instant, key \(K_1\) is closed and immediately after this the current in \(R_0\) is found to be \(I_1\). After a long time, the current attains a steady state value \(I_2\). Thereafter,\( K_2\) is closed and simultaneously \(K_1\) is opened and the voltage across \(C_0\) oscillates with amplitude \(C_0\) and angular frequency \(\omega_0\).
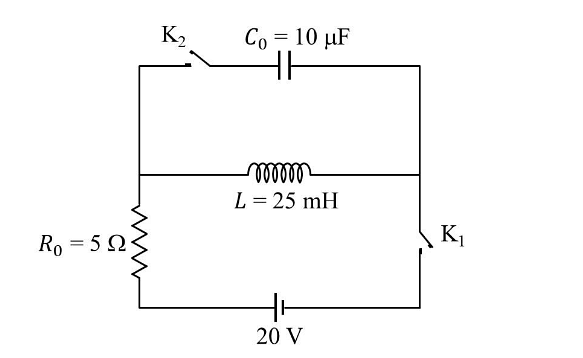
Match the quantities mentioned in List-I with their values in List-II and choose the correct option.List-I List-II P The value of \(I1\) in Ampere is I \(0\) Q The value of I2 in Ampere is II \(2\) R The value of \(\omega_0\) in kilo-radians/s is III \(4\) S The value of \(V_0\) in Volt is IV \(20\) 200 - JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- specific heat capacity
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Identify the correct statements: The presence of –NO\(_2\) group in benzene ring A. activates the ring towards electrophilic substitutions. B. deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substitutions. C. activates the ring towards nucleophilic substitutions. D. deactivates the ring towards nucleophilic substitutions. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2026
- General Chemistry
- If the distances of the point \( (1,2,a) \) from the line \[ \frac{x-1}{1}=\frac{y}{2}=\frac{z-1}{1} \] along the lines \[ L_1:\ \frac{x-1}{3}=\frac{y-2}{4}=\frac{z-a}{b} \quad \text{and} \quad L_2:\ \frac{x-1}{1}=\frac{y-2}{4}=\frac{z-a}{c} \] are equal, then \( a+b+c \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Three Dimensional Geometry
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational motion
- In an experiment, a set of readings are obtained as follows: \[ 1.24~\text{mm},\ 1.25~\text{mm},\ 1.23~\text{mm},\ 1.21~\text{mm}. \] The expected least count of the instrument used in recording these readings is _______ mm.
- JEE Main - 2026
- General Physics
Method used for separation of mixture of products (B and C) obtained in the following reaction is:

- JEE Main - 2026
- p -Block Elements
Concepts Used:
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat of a solid or liquid is the amount of heat that raises the temperature of a unit mass of the solid through 1°C.
Molar Specific Heat:
The Molar specific heat of a solid or liquid of a material is the heat that you provide to raise the temperature of one mole of solid or liquid through 1K or 1°C.
Specific Heat at Constant Pressure or Volume:
The volume of solid remains constant when heated through a small range of temperature. This is known as specific heat at a constant volume. It is denoted as CV.
The pressure of solid remains constant when heated through a small range of temperature. This is known as specific heat at constant pressure which can be denoted as CP.