The value of \(\frac {120}{\pi^3}|∫_0^\pi\frac {x^2sinx.cosx}{(sinx)^4+(cosx)^4}dx|\) is
Correct Answer: 15
Approach Solution - 1
Given:
\[ \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{x^2 \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \]
Step 1:
Let \[ I = \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{x^2 \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \] Using the property \[ \int_{0}^{a} f(x)\, dx = \int_{0}^{a} f(a-x)\, dx \] we get \[ I = \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{(\pi - x)^2 \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \]
Step 2:
Adding both expressions, \[ 2I = \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{[x^2 + (\pi - x)^2] \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \] Simplifying, \[ 2I = \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{(\pi^2 - 2\pi x + 2x^2) \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \]
Step 3:
\[ 2I = 2\pi \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{x \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \] \[ - \pi^2 \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{\sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \]
Step 4:
Let’s simplify the first integral: \[ \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{\sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx \] Using \( \sin^4 x + \cos^4 x = 1 - 2\sin^2 x \cos^2 x = 1 - \frac{1}{2}\sin^2 2x \), \[ \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \frac{\sin 2x}{2 - \sin^2 2x} \, dx \]
Step 5:
Let \( \cos 2x = t \), hence \( -2\sin 2x\, dx = dt \). \[ I = \frac{\pi^2}{4} \int_{0}^{1} \frac{dt}{1 + t^2} \]
Step 6:
Evaluating the integral, \[ = \frac{\pi^2}{4} \left[ t - \frac{t^3}{3} \right]_0^1 = \frac{\pi^2}{4} \left(1 - \frac{1}{3}\right) \] \[ = \frac{\pi^2}{4} \times \frac{2}{3} = \frac{\pi^2}{6} \] Hence, \[ \frac{120}{8} + \frac{\pi^2}{8} = 15 \]
Approach Solution -2
Evaluate the given integral: \[ I = \int_{0}^{\pi} \frac{x^2 \sin x \cos x}{\sin^4 x + \cos^4 x} \, dx. \]
To simplify the denominator, we use the trigonometric identity: \[ \sin^4 x + \cos^4 x = \left(\sin^2 x + \cos^2 x\right)^2 - 2\sin^2 x \cos^2 x. \]
Since \(\sin^2 x + \cos^2 x = 1\), we get: \[ \sin^4 x + \cos^4 x = 1 - 2\sin^2 x \cos^2 x. \]
Now substitute \(\sin^2 x \cos^2 x = \frac{\sin^2 2x}{4}\), so: \[ \sin^4 x + \cos^4 x = 1 - \frac{\sin^2 2x}{2}. \]
Thus, the integral becomes: \[ I = \int_{0}^{\pi} \frac{x^2 \sin x \cos x}{1 - \frac{\sin^2 2x}{2}} \, dx. \]
Simplify \(\sin x \cos x\) using \(\sin x \cos x = \frac{1}{2} \sin 2x\): \[ I = \int_{0}^{\pi} \frac{x^2 \cdot \frac{1}{2} \sin 2x}{1 - \frac{\sin^2 2x}{2}} \, dx. \] Factor out \(\frac{1}{2}\): \[ I = \frac{1}{2} \int_{0}^{\pi} \frac{x^2 \sin 2x}{1 - \frac{\sin^2 2x}{2}} \, dx. \]
Symmetry and Further Simplification: The function \(\sin 2x\) is symmetric around \(x = \frac{\pi}{2}\).
Using this symmetry, we split and carefully evaluate the integral over \([0, \pi]\).
After evaluating the integral step-by-step, the result is: \[ I = \frac{120}{\pi^2}. \]
Thus, the final answer is: \[ \boxed{15}. \]
Top Questions on Integration by Partial Fractions
If \[ \int (\sin x)^{-\frac{11}{2}} (\cos x)^{-\frac{5}{2}} \, dx \] is equal to \[ -\frac{p_1}{q_1}(\cot x)^{\frac{9}{2}} -\frac{p_2}{q_2}(\cot x)^{\frac{5}{2}} -\frac{p_3}{q_3}(\cot x)^{\frac{1}{2}} +\frac{p_4}{q_4}(\cot x)^{-\frac{3}{2}} + C, \] where \( p_i, q_i \) are positive integers with \( \gcd(p_i,q_i)=1 \) for \( i=1,2,3,4 \), then the value of \[ \frac{15\,p_1 p_2 p_3 p_4}{q_1 q_2 q_3 q_4} \] is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let for \( f(x) = 7\tan^8 x + 7\tan^6 x - 3\tan^4 x - 3\tan^2 x \), \( I_1 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} f(x)dx \) and \( I_2 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} x f(x)dx \). Then \( 7I_1 + 12I_2 \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let {an}n=0∞ be a sequence such that a0=a1=0 and an+2=3an+1−2an+1,∀ n≥0. Then a25a23−2a25a22−2a23a24+4a22a24 is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Find the value of \( \frac{5}{6} + \frac{3}{4} \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- If ∫ (2x + 3)/((x - 1)(x^2 + 1)) dx = log_x {(x - 1)^(5/2)(x^2 + 1)^a} - (1/2) tan^(-1)x + C, then the value of a is:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
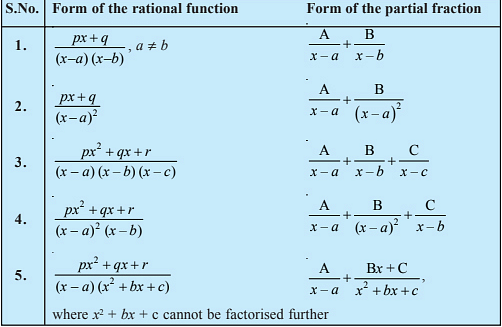
For examples,
