Match List I with List IILIST I LIST II A Gauss's Law in Electrostatics I \(\oint \vec{E} \cdot d \vec{l}=-\frac{d \phi_B}{d t}\) B Faraday's Law II \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{A}=0\) C Gauss's Law in Magnetism III \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l}=\mu_0 i_c+\mu_0 \in_0 \frac{d \phi_E}{d t}\) D Ampere-Maxwell Law IV \(\oint \vec{E} \cdot d \vec{s}=\frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| LIST I | LIST II | ||
| A | Gauss's Law in Electrostatics | I | \(\oint \vec{E} \cdot d \vec{l}=-\frac{d \phi_B}{d t}\) |
| B | Faraday's Law | II | \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{A}=0\) |
| C | Gauss's Law in Magnetism | III | \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l}=\mu_0 i_c+\mu_0 \in_0 \frac{d \phi_E}{d t}\) |
| D | Ampere-Maxwell Law | IV | \(\oint \vec{E} \cdot d \vec{s}=\frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\) |
- A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
- A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
- A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
- A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
Gauss's Law of electrostatic
Faraday's law
Gauss's law of magnetism
Ampere's Maxwell law
Where : Conduction current
: Displacement current
Approach Solution -2
Applying the definitions of the laws:
Gauss's Law in Electrostatics: \( \oint \mathbf{E} \cdot d\mathbf{s} = \frac{q}{\epsilon_0} \).
Faraday's Law: \( \oint \mathbf{E} \cdot d\mathbf{l} = -\frac{d\Phi_B}{dt} \).
Gauss's Law in Magnetism: \( \oint \mathbf{B} \cdot d\mathbf{A} = 0 \).
Ampere-Maxwell Law: \( \oint \mathbf{B} \cdot d\mathbf{l} = \mu_0 i_c + \mu_0 \epsilon_0 \frac{d\Phi_E}{dt} \).
Final Answer: A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
Top Questions on Gauss Law
- If the net flux through a cube is 1.05 N m\(^2\) C\(^{-1}\), what will be the total charge inside the cube? (Given: The permittivity of free space is \(8.85 \times 10^{-12}\) C\(^2\) N\(^{-1}\) m\(^{-2}\)).
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Physics
- Gauss Law
- A charge q is placed at the center of one of the surface of a cube. The flux linked with the cube is :-
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Gauss Law
- An electric field \( \vec{E} = (2x \hat{i}) \, \text{N C}^{-1} \) exists in space. A cube of side \( 2 \, \text{m} \) is placed in the space as per the figure given below. The electric flux through the cube is __________ \( \text{N m}^2/\text{C} \).
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Gauss Law
- There are two cubical Gaussian surface carrying charges as shown. Find ratio of fluxes through surface \(C_1\) and \(C_2\):

- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Gauss Law
- A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length a = 10 cm. Electric field lines are parallel to x-axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces ABCD and EFGH are 6kNC-1 and 9kNC-1 respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is
[Take ε0 = 9 × 10-12 Fm-1]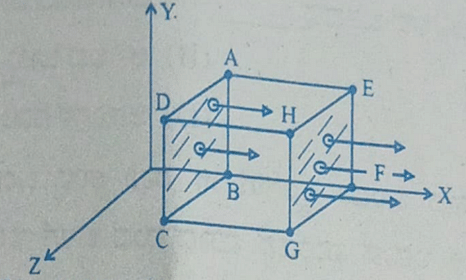
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Gauss Law
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Gauss Law
Gauss law states that the total amount of electric flux passing through any closed surface is directly proportional to the enclosed electric charge.
Gauss Law:
According to the Gauss law, the total flux linked with a closed surface is 1/ε0 times the charge enclosed by the closed surface.

For example, a point charge q is placed inside a cube of edge ‘a’. Now as per Gauss law, the flux through each face of the cube is q/6ε0.
Gauss Law Formula:
As per the Gauss theorem, the total charge enclosed in a closed surface is proportional to the total flux enclosed by the surface. Therefore, if ϕ is total flux and ϵ0 is electric constant, the total electric charge Q enclosed by the surface is;
Q = ϕ ϵ0
The Gauss law formula is expressed by;
ϕ = Q/ϵ0
Where,
Q = total charge within the given surface,
ε0 = the electric constant.