Let P(a, b) be a point on the parabola y2 = 8x such that the tangent at P passes through the centre of the circle x2 + y2 – 10x – 14y + 65 = 0. Let A be the product of all possible values of a and B be the product of all possible values of b. Then the value of A + B is equal to
- 0
- 25
- 40
- 65
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
To solve this problem, we need to consider a point \(P(a, b)\) on the parabola \(y^2 = 8x\). We know that the tangent at this point passes through the center of the given circle \(x^2 + y^2 - 10x - 14y + 65 = 0\).
First, let's find the center of the circle. The equation of the circle can be rewritten in the standard form by completing the square:
\(x^2 - 10x + y^2 - 14y = -65\)
Complete the square for \(x\) and \(y\):
\((x-5)^2 - 25 + (y-7)^2 - 49 = -65\)
Solving, we have:
\((x-5)^2 + (y-7)^2 = 9\)
So, the center of the circle is \((5, 7)\).
The equation of the parabola is \(y^2 = 8x\). For a point \(P(a, b)\) on the parabola, we have \(b^2 = 8a\).
The equation of the tangent to the parabola at \(P(a, b)\) is obtained using the point form of the tangent equation:
\(yb = 4(x + a)\) (using \(T = 0\) formula for tangents)
This tangent passes through the center of the circle \((5, 7)\), so substitute these values into the tangent equation:
\(7b = 4(5 + a)\)
Solving this, we get:
\(7b = 20 + 4a\)
Thus, \(4a = 7b - 20 \; \Longrightarrow \; a = \frac{7b - 20}{4}\)
Also, recall \(b^2 = 8a\). Substitute the value of \(a\) we obtained:
\(b^2 = 8\left(\frac{7b - 20}{4}\right)\)
\(b^2 = 2(7b - 20)\)
Equating, we get:
\(b^2 = 14b - 40\)
Rearranging gives:
\(b^2 - 14b + 40 = 0\)
Solving this quadratic equation using the formula \(b = \frac{-B \pm \sqrt{B^2 - 4AC}}{2A}\), where \(A = 1\), \(B = -14\), \(C = 40\), we find:
\(b = \frac{14 \pm \sqrt{14^2 - 4 \times 1 \times 40}}{2}\)
\(b = \frac{14 \pm \sqrt{196 - 160}}{2}\)
\(b = \frac{14 \pm \sqrt{36}}{2}\)
\(b = \frac{14 \pm 6}{2}\)
The possible values of \(b\) are \(b = 10\) and \(b = 4\).
For each value of \(b\), calculate \(a\) using \(a = \frac{7b - 20}{4}\):
- When \(b = 10\), \(a = \frac{7 \cdot 10 - 20}{4} = \frac{50}{4} = 12.5\)
- When \(b = 4\), \(a = \frac{7 \cdot 4 - 20}{4} = \frac{8}{4} = 2\)
The product of all possible values of \(a\) is \(A = 12.5 \times 2 = 25\).
The product of all possible values of \(b\) is \(B = 10 \times 4 = 40\).
Therefore, the required sum \(A + B = 25 + 40 = 65\).
Thus, the value of \(A + B\) is 65.
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is (D):
Centre of circle x2 + y2 – 10x –14y + 65 = 0 is at (5, 7).
Let the equation of tangent to y2 = 8x is
yt = x + 2t2
which passes through (5, 7)
7t = 5 + 2t2
⇒ 2t2 – 7t + 5 = 0
t = 1, \(\frac{5}{2}\)
A = 1×12×2×(\(\frac{5}{2}\))2
= 25
B = 2×2×1×2×2×\(\frac{5}{2}\)
= 40
A+B = 65
Top Questions on Integration by Partial Fractions
If \[ \int (\sin x)^{-\frac{11}{2}} (\cos x)^{-\frac{5}{2}} \, dx \] is equal to \[ -\frac{p_1}{q_1}(\cot x)^{\frac{9}{2}} -\frac{p_2}{q_2}(\cot x)^{\frac{5}{2}} -\frac{p_3}{q_3}(\cot x)^{\frac{1}{2}} +\frac{p_4}{q_4}(\cot x)^{-\frac{3}{2}} + C, \] where \( p_i, q_i \) are positive integers with \( \gcd(p_i,q_i)=1 \) for \( i=1,2,3,4 \), then the value of \[ \frac{15\,p_1 p_2 p_3 p_4}{q_1 q_2 q_3 q_4} \] is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let for \( f(x) = 7\tan^8 x + 7\tan^6 x - 3\tan^4 x - 3\tan^2 x \), \( I_1 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} f(x)dx \) and \( I_2 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} x f(x)dx \). Then \( 7I_1 + 12I_2 \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let {an}n=0∞ be a sequence such that a0=a1=0 and an+2=3an+1−2an+1,∀ n≥0. Then a25a23−2a25a22−2a23a24+4a22a24 is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Find the value of \( \frac{5}{6} + \frac{3}{4} \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- If ∫ (2x + 3)/((x - 1)(x^2 + 1)) dx = log_x {(x - 1)^(5/2)(x^2 + 1)^a} - (1/2) tan^(-1)x + C, then the value of a is:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
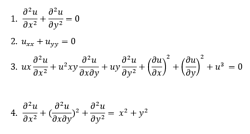
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
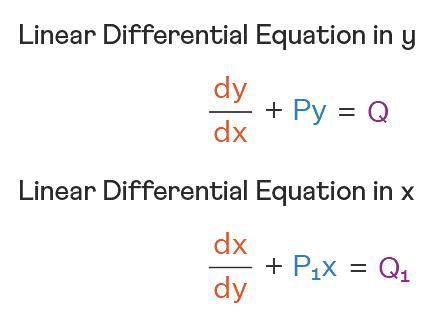
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations