Question:
If \(\begin{array}{l}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{3}}\frac{15x^3}{\sqrt{1+x^2 + \sqrt{(1+x^2)^3}}}dx = \alpha \sqrt{2}+\beta\sqrt{3},\end{array}\)where \(α, β\) are integers, then \(α + β\) is equal to
If \(\begin{array}{l}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{3}}\frac{15x^3}{\sqrt{1+x^2 + \sqrt{(1+x^2)^3}}}dx = \alpha \sqrt{2}+\beta\sqrt{3},\end{array}\)where \(α, β\) are integers, then \(α + β\) is equal to
Updated On: Dec 31, 2025
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Solution and Explanation
Put
\[\begin{array}{l} x = \tan \theta \Rightarrow dx = \sec^2 \theta \, d\theta \end{array}\]\[\Rightarrow I = \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{3}} \frac{15 \tan^3 \theta \cdot \sec^2 \theta \, d\theta}{\sqrt{1 + \tan^2 \theta + \sqrt{\sec^6 \theta}}}\]\[\Rightarrow I = \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{3}} \frac{15 \tan^2 \theta \sec^2 \theta \, d\theta}{\sec \theta \sqrt{1 + \sec \theta}}\]\[\Rightarrow I = \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{3}} \frac{15 (\sec^2 \theta - 1) \sec \theta \tan \theta \, d\theta}{\sqrt{1 + \sec \theta}}\]Now put \(1 + \sec \theta = t^2\)
\[\Rightarrow \sec \theta \tan \theta \, d\theta = 2t \, dt\]\[\Rightarrow I = \int_{\sqrt{2}}^{\sqrt{3}} \frac{15 \left( (t^2 - 1)^2 - 1 \right) 2t \, dt}{t}\]\[\Rightarrow I = 30 \int_{\sqrt{2}}^{\sqrt{3}} \left( t^4 - 2t^2 + 1 - 1 \right) dt\]\[\Rightarrow I = 30 \int_{\sqrt{2}}^{\sqrt{3}} \left( t^4 - 2t^2 \right) dt\]\[\Rightarrow I = 30 \left( \frac{t^5}{5} - \frac{2t^3}{3} \right)_{\sqrt{2}}^{\sqrt{3}}\]\[= 30 \left[ \left( \frac{9}{5} \sqrt{3} - 2 \sqrt{3} \right) - \left( \frac{4 \sqrt{2}}{5} - \frac{4 \sqrt{2}}{3} \right) \right]\]\[= (54 \sqrt{3} - 60 \sqrt{3}) - (24 \sqrt{2} - 40 \sqrt{2})\]\[= 16 \sqrt{2} - 6 \sqrt{3}\]\[\therefore \alpha = 16 \text{ and } \beta = -6\]\[\alpha + \beta = 10\]Was this answer helpful?
2
1
Top Questions on Integration by Partial Fractions
If \[ \int (\sin x)^{-\frac{11}{2}} (\cos x)^{-\frac{5}{2}} \, dx \] is equal to \[ -\frac{p_1}{q_1}(\cot x)^{\frac{9}{2}} -\frac{p_2}{q_2}(\cot x)^{\frac{5}{2}} -\frac{p_3}{q_3}(\cot x)^{\frac{1}{2}} +\frac{p_4}{q_4}(\cot x)^{-\frac{3}{2}} + C, \] where \( p_i, q_i \) are positive integers with \( \gcd(p_i,q_i)=1 \) for \( i=1,2,3,4 \), then the value of \[ \frac{15\,p_1 p_2 p_3 p_4}{q_1 q_2 q_3 q_4} \] is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let for \( f(x) = 7\tan^8 x + 7\tan^6 x - 3\tan^4 x - 3\tan^2 x \), \( I_1 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} f(x)dx \) and \( I_2 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} x f(x)dx \). Then \( 7I_1 + 12I_2 \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let {an}n=0∞ be a sequence such that a0=a1=0 and an+2=3an+1−2an+1,∀ n≥0. Then a25a23−2a25a22−2a23a24+4a22a24 is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Find the value of \( \frac{5}{6} + \frac{3}{4} \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- If ∫ (2x + 3)/((x - 1)(x^2 + 1)) dx = log_x {(x - 1)^(5/2)(x^2 + 1)^a} - (1/2) tan^(-1)x + C, then the value of a is:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A gas of certain mass filled in a closed cylinder at a pressure of $3.23\,\text{kPa}$ has temperature $50^\circ$C. The gas is now heated to double its temperature. The modified pressure is ___ Pa.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- Let the circle \(x^2+y^2=4\) intersect the \(x\)-axis at points \(A(a,0)\) and \(B(b,0)\). Let \(P(2\cos\alpha,2\sin\alpha)\), \(0<\alpha<\frac{\pi}{2}\), and \(Q(2\cos\beta,2\sin\beta)\) be two points on the circle such that \((\alpha-\beta)=\frac{\pi}{2}\). Then the point of intersection of lines \(AQ\) and \(BP\) lies on:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Circles
- The moment of inertia of a square loop made of four uniform solid cylinders, each having radius R and length L (\(R \le L\)) about an axis passing through the mid points of opposite sides, is (Take the mass of the entire loop as M) :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Kinematics
- When a light of a given wavelength falls on a metallic surface the stopping potential for photoelectrons is \(3.2\ \text{V}\). If a second light having wavelength twice of the first light is used, the stopping potential drops to \(0.7\ \text{V}\). The wavelength of the first light is ________ m.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Photoelectric Effect
- An infinitely long straight wire carrying current $I$ is bent in a planar shape as shown in the diagram. The radius of the circular part is $r$. The magnetic field at the centre $O$ of the circular loop is :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Current electricity
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
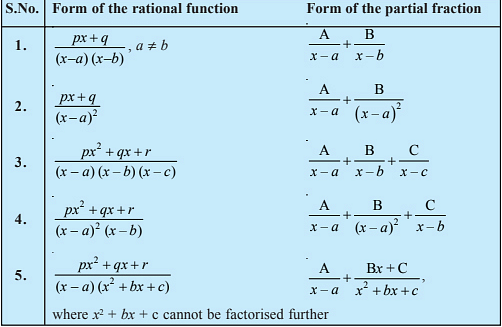
For examples,
