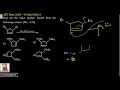
Find out the major product formed from the following reaction.\([ \text{Me: } -\text{CH}_3 ]\)

The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation

Step 1: Nucleophilic substitution (\( S_N2 \)) with dimethylamine (\( \text{Me}_2\text{NH} \)): The bromine atom at one of the carbons is replaced by the nucleophile (\( \text{Me}_2\text{N} \)) via an \( S_N2 \) mechanism. This forms an intermediate with a quaternary amine at the adjacent carbon.
Step 2: Deprotonation: The positively charged intermediate loses a proton (\(-\text{H}^+\)) to stabilize the structure, forming an alkene.
Step 3: Second \( S_N2 \) reaction: The second equivalent of dimethylamine attacks the adjacent carbon-bromine bond, substituting the bromine atom with another \( \text{Me}_2\text{N} \) group.
The final product contains two \( \text{Me}_2\text{N} \) groups attached to the cyclopentane ring at adjacent positions.
The above mechanism is valid for both cis and trans isomers. Hence, the products are the same for both.
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
- The correct order of reactivity of CH$_3$Br in methanol with the following nucleophiles is
$ \mathrm{F^- ,\ I^- ,\ C_2H_5O^- \ and\ C_6H_5O^- }$- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
The major product (A) is:

- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
- When sec-butylcyclohexane reacts with bromine in the presence of sunlight, the major product is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
- What is the correct sequence of increasing reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic addition reaction? (A) Ethanal
(B) Propanone
(C) Propanal
(D) Butanone- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
- Optically active alkyl halide undergoing S\(_N\)2 substitution involves
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions (both aromatic and aliphatic)
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}-\hat{j}-\hat{k}$, $\vec{b}=\hat{i}+3\hat{j}-\hat{k}$ and $\vec{c}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}$. Let $\vec{v}$ be the vector in the plane of $\vec{a}$ and $\vec{b}$, such that the length of its projection on the vector $\vec{c}$ is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{14}}$. Then $|\vec{v}|$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Vector Algebra
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration