Question:
The variation of induced emf (e) with time (t) in a coil if a
short bar magnet is moved along its axis with a constant
velocity is best represented as
The variation of induced emf (e) with time (t) in a coil if a
short bar magnet is moved along its axis with a constant
velocity is best represented as
Updated On: Jul 14, 2022
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Polarity of emf will be opposite in the two cases while
entering and while leaving the coil. Only in option
(b) polarity is changing. Hence, the correct option is (b).
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Faradays laws of induction
- In a coil, the current changes form –2 A to +2A in 0.2 s and induces an emf of 0.1 V. The self-inductance of the coil is :
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- The magnetic flux \(\phi\) (in weber) linked with a closed circuit of resistance \(8 \, \Omega\) varies with time (in seconds) as \(\phi = 5t^2 - 36t + 1\). The induced current in the circuit at \(t = 2 \, \text{s}\) is ______ A.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A square loop of side 2 cm enters a magnetic field with a constant speed of 2 cm s-1 as shown. The front edge enters the field at t = 0s. Which of the following graph correctly depicts the induced emf in the loop?
( Take clockwise direction positive )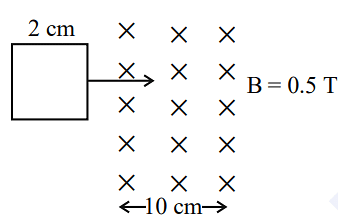
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A metallic rod of length 1 m held along east-west direction is allowed to fall down freely. Given horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field BH = 3 × 10-5 T. The emf induced in the rod at an instant t = 2s after it is released is ( Take g = 10 ms-2 )
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- The current following through an inductance coil of self inductance 6 mH at different time instants is as shown. The emf induced between t = 20s and t = 40s is nearly
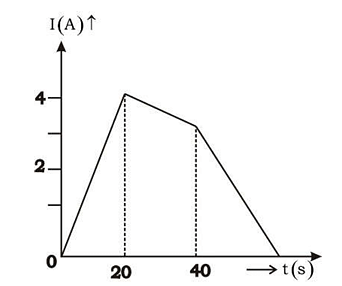
- KCET - 2021
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
View More Questions
Questions Asked in IIT JEE exam
Proton (P) and electron (e) will have same de-Broglie wavelength when the ratio of their momentum is (assume mp = 1849me):
- IIT JEE - 2023
- Stereoisomers
- If the weight of an object on earth's surface is 400 N, then weight of the same particle at a depth \(\frac{R}{2}\) from surface would be (R is radius of earth)
- IIT JEE - 2023
- Stereoisomers
- The major product of the following reaction is

- IIT JEE - 2022
- Hydrocarbons
- Let $ \alpha ( a) \, and \, \beta (a) $ be the roots of the equation $ (\sqrt [3] {1 + a} - 1) x^2 - (\sqrt {1 + a} - 1) x + (\sqrt [ 6] {1 + a} - 1) = 0$, where a > - 1. Then, $ lim_{a \to 0^+ } $, $ \alpha (a) \, and \, lim_{a \to 0^+ } \beta $ (a) are
- IIT JEE - 2012
- Quadratic Equations
- Let $f:(-1,1)\rightarrow$ R be such that $f(cos 4 \theta)=\frac{2}{2-sec^2 \theta}$ for $\theta \in \Bigg(0,\frac{\pi}{4}\Bigg)\cup\Bigg(\frac{\pi}{4},\frac{\pi}{2}\Bigg).$ Then, the value(s) of $f\Bigg(\frac{1}{3}\Bigg)$ is are
- IIT JEE - 2012
- Functions
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Faradays Laws of Induction
There are two laws, given by Faraday which explain the phenomena of electromagnetic induction:
Faraday's First Law:
Whenever a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field, an emf is induced. If the conductor circuit is closed, a current is induced, known as the induced current.
Faraday's Second Law:
The Emf induced inside a coil is equal to the rate of change of associated magnetic flux.
This law can be mathematically written as:
∈\(-N {\triangle \phi \over \triangle t}\)




