The magnetic flux \(\phi\) (in weber) linked with a closed circuit of resistance \(8 \, \Omega\) varies with time (in seconds) as \(\phi = 5t^2 - 36t + 1\). The induced current in the circuit at \(t = 2 \, \text{s}\) is ______ A.
Correct Answer: 2
Approach Solution - 1
To find the induced current in the circuit at \( t = 2 \, \text{s} \), we first need to determine the electromotive force (emf) induced in the circuit using Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction. The emf (\( \varepsilon \)) is given by the negative rate of change of magnetic flux (\( \phi \)) with respect to time, \( \varepsilon = -\frac{d\phi}{dt} \). Given \( \phi = 5t^2 - 36t + 1 \), we differentiate: \(\frac{d\phi}{dt} = \frac{d}{dt}(5t^2 - 36t + 1) = 10t - 36\).
Substitute \( t = 2 \) into the derivative:
\(\left.\frac{d\phi}{dt}\right|_{t=2} = 10(2) - 36 = 20 - 36 = -16 \, \text{Wb/s}.\)
The induced emf is \(\varepsilon = -\left(-16\right) = 16 \, \text{V}.\)
Using Ohm's Law, \( I = \frac{\varepsilon}{R} \), with resistance \( R = 8 \, \Omega \):
\( I = \frac{16}{8} = 2 \, \text{A}.\)
The computed current, \( 2 \, \text{A} \), fits the expected range of 2 to 2 A. Therefore, the induced current at \( t = 2 \, \text{s} \) is \( 2 \, \text{A}. \)
Approach Solution -2
The emf \( \varepsilon \) induced in the circuit is given by Faraday’s law:
\[ \varepsilon = -\frac{d\Phi}{dt}. \]Calculate \( \frac{d\Phi}{dt} \):
\[ \frac{d\Phi}{dt} = 10t - 36. \]At \( t = 2 \, \text{s} \):
\[ \varepsilon = -(10 \cdot 2 - 36) = -(-16) = 16 \, \text{V}. \]The induced current \( i \) in the circuit is:
\[ i = \frac{\varepsilon}{R} = \frac{16}{8} = 2 \, \text{A}. \]Thus, the induced current at \( t = 2 \, \text{s} \) is:
\[ 2 \, \text{A}. \]Top Questions on Faradays laws of induction
- In a coil, the current changes form –2 A to +2A in 0.2 s and induces an emf of 0.1 V. The self-inductance of the coil is :
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A square loop of side 2 cm enters a magnetic field with a constant speed of 2 cm s-1 as shown. The front edge enters the field at t = 0s. Which of the following graph correctly depicts the induced emf in the loop?
( Take clockwise direction positive )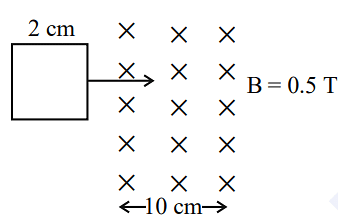
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A metallic rod of length 1 m held along east-west direction is allowed to fall down freely. Given horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field BH = 3 × 10-5 T. The emf induced in the rod at an instant t = 2s after it is released is ( Take g = 10 ms-2 )
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- The current following through an inductance coil of self inductance 6 mH at different time instants is as shown. The emf induced between t = 20s and t = 40s is nearly
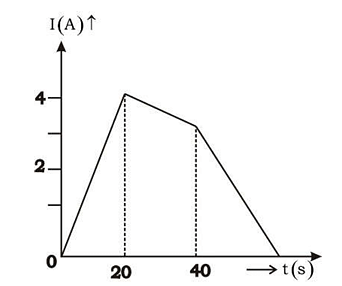
- KCET - 2021
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A wheel with $20$ metallic spokes each $1\, m$ long is rotated with a speed of $120\, rpm$ in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of $0.4\, G$. The induced emf between the axle and rim of the wheel will be, $(1 G = 10^{-4}\, T)$
- NEET (UG) - 2020
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter