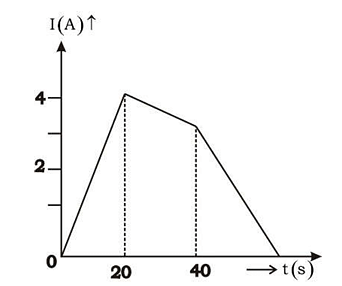
The current following through an inductance coil of self inductance 6 mH at different time instants is as shown. The emf induced between t = 20s and t = 40s is nearly

- 2 × 10-2 V
- 3 × 10-4 V
- 4 × 10-3 V
- 30 × 102 V
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
The equations describe the induced electromotive force (emf) in a circuit:
\[ |e| = L \frac{dI}{dt} \]
The magnitude of the emf (\(|e|\)) is given by the product of inductance (\(L\)) and the rate of change of current (\(\frac{dI}{dt}\)).
\[ |e| = 6 \times 10^{-3} \left[ \frac{I_2 - I_1}{t_2 - t_1} \right] \]
Substituting the values, the emf is calculated using the discrete current change over time.
\[ |e| = 6 \times 10^{-3} \left[ \frac{1}{40 - 20} \right] \]
Plugging in the specific time interval (\(t_1 = 20\), \(t_2 = 40\)) and assuming the current change (\(\Delta I = 1\)).
\[ e = 3 \times 10^{-4} \text{ V} \]
The final result for the induced emf is \(3 \times 10^{-4}\) volts.
Approach Solution -2
The self-inductance of the coil is given as $L = 6 \, \text{mH} = 6 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{H}$.
The induced emf in an inductor is given by Faraday's Law of induction:
$e = -L \frac{dI}{dt}$
From the graph, we need to find the rate of change of current $\frac{dI}{dt}$ between $t = 20 \, \text{s}$ and $t = 40 \, \text{s}$.
At $t = 20 \, \text{s}$, the current $I_1 = 4 \, \text{A}$.
At $t = 40 \, \text{s}$, the current $I_2 = 3 \, \text{A}$.
The change in current $\Delta I = I_2 - I_1 = 3 - 4 = -1 \, \text{A}$.
The change in time $\Delta t = 40 - 20 = 20 \, \text{s}$.
The rate of change of current $\frac{dI}{dt} \approx \frac{\Delta I}{\Delta t} = \frac{-1 \, \text{A}}{20 \, \text{s}} = -0.05 \, \text{A/s}$.
Now, we calculate the induced emf:
$e = -L \frac{dI}{dt} = -(6 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{H}) \times (-0.05 \, \text{A/s})$
$e = 6 \times 10^{-3} \times 0.05 \, \text{V}$
$e = 0.3 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{V} = 3 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{V}$.
Top Questions on Faradays laws of induction
- In a coil, the current changes form –2 A to +2A in 0.2 s and induces an emf of 0.1 V. The self-inductance of the coil is :
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- The magnetic flux \(\phi\) (in weber) linked with a closed circuit of resistance \(8 \, \Omega\) varies with time (in seconds) as \(\phi = 5t^2 - 36t + 1\). The induced current in the circuit at \(t = 2 \, \text{s}\) is ______ A.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A square loop of side 2 cm enters a magnetic field with a constant speed of 2 cm s-1 as shown. The front edge enters the field at t = 0s. Which of the following graph correctly depicts the induced emf in the loop?
( Take clockwise direction positive )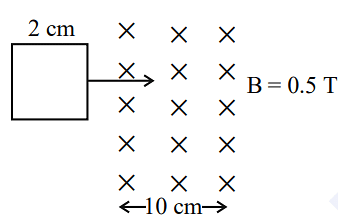
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A metallic rod of length 1 m held along east-west direction is allowed to fall down freely. Given horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field BH = 3 × 10-5 T. The emf induced in the rod at an instant t = 2s after it is released is ( Take g = 10 ms-2 )
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
- A wheel with $20$ metallic spokes each $1\, m$ long is rotated with a speed of $120\, rpm$ in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of $0.4\, G$. The induced emf between the axle and rim of the wheel will be, $(1 G = 10^{-4}\, T)$
- NEET (UG) - 2020
- Physics
- Faradays laws of induction
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives