The electric flux from a cube of side 1 m is \(\Phi\). When the side of the cube is made 3 m and the charge enclosed by the cube is made one-third of the original value, then the flux from the bigger cube will be:
Show Hint
- \(\Phi\)
- \(\Phi/3\)
- \(3 \Phi\)
- \(9 \Phi\)
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Electric Flux
A line charge of length \( \frac{a}{2} \) is kept at the center of an edge BC of a cube ABCDEFGH having edge length \( a \). If the density of the line is \( \lambda C \) per unit length, then the total electric flux through all the faces of the cube will be : (Take \( \varepsilon_0 \) as the free space permittivity)

- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- An electric field \( \vec{E} \) is given by:
\[ \vec{E} = \begin{cases} +100\, \hat{i} \dfrac{\text{N}}{\text{C}} & \text{for } x>0 \\ -100\, \hat{i} \dfrac{\text{N}}{\text{C}} & \text{for } x<0 \end{cases} \] A right circular cylinder of length \( 10\, \text{cm} \) and radius \( 2\, \text{cm} \), is placed such that its axis coincides with the x-axis and its two faces are at \( x = -5\, \text{cm} \) and \( x = 5\, \text{cm} \). Calculate: (a) the net outward flux through the cylinder, and (b) the net charge inside the cylinder.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
A metallic sphere of radius \( R \) carrying a charge \( q \) is kept at a certain distance from another metallic sphere of radius \( R_4 \) carrying a charge \( Q \). What is the electric flux at any point inside the metallic sphere of radius \( R \) due to the sphere of radius \( R_4 \)?

- KCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- The angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in a transverse wave is (except when the particle passes through the mean position)
- KCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- A charge is kept at the central point P of a cylindrical region. The two edges subtend a half-angle \(\theta\) at P, as shown in the figure. When \(\theta = 30\) , then the electric flux through the curved surface of the cylinder is \(Φ\). If \(\theta= 60\degree\) , then the electric flux through the curved surface becomes \(Φ/√𝑛\), where the value of n is______.
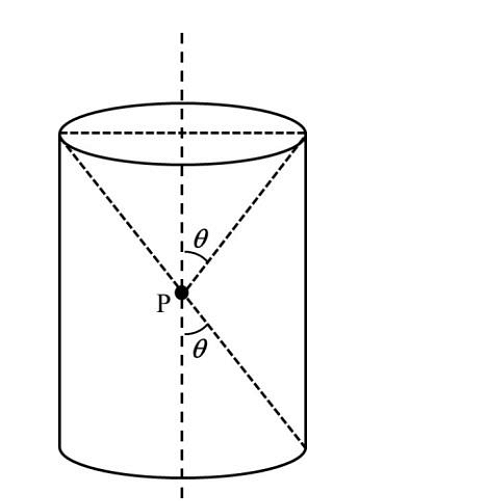
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Flux
Questions Asked in COMEDK UGET exam
- Given that the freezing point of benzene is $ 5.48^\circ C $ and its $ K_f $ value is $ 5.12^\circ C/m $, what would be the freezing point of a solution of 20 g of propane in 400 g of benzene?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
200 ml of an aqueous solution contains 3.6 g of Glucose and 1.2 g of Urea maintained at a temperature equal to 27$^{\circ}$C. What is the Osmotic pressure of the solution in atmosphere units?
Given Data R = 0.082 L atm K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$
Molecular Formula: Glucose = C$_6$H$_{12}$O$_6$, Urea = NH$_2$CONH$_2$- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
- An inorganic compound W undergoes the following reactions: $ W + \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \xrightarrow{\text{O}_2 / \text{heat}} X + H^+ \xrightarrow{} Y(s) $ $ Y(aq) + \text{KCl} (aq) \xrightarrow{} Z(s) $ Z appears in the form of orange crystals and is used as an oxidising agent in acid medium. Identify the compound W.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- coordination compounds
- A current of 3.0 A is passed through 750 ml of 0.45 M solution of CuSO₄ for 2 hours with a current efficiency of 90\%. If the volume of the solution is assumed to remain constant, what would be the final molarity of CuSO₄ solution?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Solutions
- For a reaction $ 5X + Y \to 3Z $, the rate of formation of Z is $ 2.4 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{mol L}^{-1} \text{s}^{-1} $. Calculate the average rate of disappearance of X.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations