Question:
Observe the following equilibrium at T(K)
\[
H_2(g) + I_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2HI(g)
\]
Which one of the following does not disturb the above equilibrium?
Observe the following equilibrium at T(K)
\[
H_2(g) + I_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2HI(g)
\]
Which one of the following does not disturb the above equilibrium?
Show Hint
Le Chatelier's Principle states that adding or removing reactants/products will shift the equilibrium. Inert gases do not affect the equilibrium position.
Updated On: May 15, 2025
- Addition of \( H_2(g) \)
- Removal of \( HI(g) \)
- Addition of \( I_2(g) \)
- Addition of \( He(g) \)
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
This question is related to Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in concentration, pressure, or temperature, the system will shift in such a direction as to counteract the change and restore equilibrium.
Let's analyze each option:
- Option (1): Addition of \( H_2(g) \) – This will shift the equilibrium towards the right (formation of more \( HI(g) \)) to counteract the increase in \( H_2 \).
- Option (2): Removal of \( HI(g) \) – This will also shift the equilibrium towards the right to produce more \( HI(g) \).
- Option (3): Addition of \( I_2(g) \) – Similar to option (1), this will shift the equilibrium towards the right to counteract the increase in \( I_2 \).
- Option (4): Addition of \( He(g) \) – Helium is an inert gas that does not react with the other gases in the equilibrium. Adding an inert gas does not affect the equilibrium position because it does not change the partial pressures of the reactants or products.
Thus, the correct answer is \( \boxed{\text{Addition of He(g)}} \).
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Chemical equilibria
- The ratio of osmotic pressures of aqueous solutions of 0.01 M BaCl2 to 0.005 M NaCl is
[Given: Both compounds dissociate completely in water]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- A 1.0 L solution is prepared by dissolving 2.0 g of benzoic acid and 4.0 g of sodium benzoate in water. The pH of the resulting solution is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
Given: Molar mass of benzoic acid is 122 g mol−1
Molar mass of sodium benzoate is 144 g mol−1
p𝐾a of benzoic acid is 4.2- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- 0.1 M aqueous solution of a weak monobasic acid has pH 2.0. The pKa of the monobasic acid is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- Consider the exothermic chemical reaction O2(𝑔)+2H2(𝑔) ⇌ 2H2O(𝑔) at equilibrium in a closed container. The correct statement(s) is/are
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is ______.
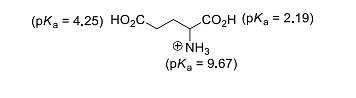
(round off to two decimal places)- IIT JAM CY - 2023
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
View More Questions
Questions Asked in AP EAPCET exam
- In a series LCR circuit, the voltages across the capacitor, resistor, and inductor are in the ratio 2:3:6. If the voltage of the source in the circuit is 240 V, then the voltage across the inductor is
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Electromagnetic induction
- 0.25 moles of $ \text{CH}_2\text{FCOOH} $ was dissolved in $ 0.5 \, \text{kg} $ of water. The depression in freezing point of the resultant solution was observed as $ 1^\circ \text{C} $. What is the van't Hoff factor? ($ K_f = 1.86 \, \text{K kg mol}^{-1} $)
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- At $T(K)$, the vapor pressure of water is $x$ kPa. What is the vapor pressure (in kPa) of 1 molal solution containing non-volatile solute?
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- At 300 K, vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 70 mm Hg. It forms an ideal solution with liquid B. Mole fraction of B = 0.2 and total vapour pressure of solution = 84 mm Hg. What is vapour pressure (in mm) of pure B?
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- A 1% (w/v) aqueous solution of a certain solute is isotonic with a 3% (w/v) solution of glucose (molar mass 180 g mol$^{-1}$). The molar mass of solute (in g mol$^{-1}$) is
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
View More Questions