Let $f: R \rightarrow R$ be defined as,
$f(x) =
\begin{cases}
-55x, & \text{if } x < -5 \\
2x^3 -3x^2 -120x, & \text{if } 5 \le x \le 4 \\
2x^3 -3x^2-36x-336& \text{if } x > 4,
\end{cases} $
Let $A=\{ x \in R : f$ is increasing $\} .$ Then $A$ is equal to
- $(-\infty,-5) \cup(4, \infty)$
- $(-5, \infty)$
- $(-\infty,-5) \cup(-4, \infty)$
- (-5,-4)$\cup(4, \infty)$
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
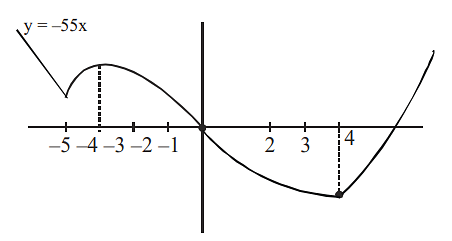
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is (D) : (-5,-4)\(\cup(4, \infty)\)
For f'(x) ≥ 0
Case I :- -5 < x < 4
Then f'(x) ≥ 0 ≥ 0 implies
6x2 - 6x - 120 ≥ 0
⇒ x2 - x - 20 ≥ 0
⇒ (x - 5) (x + 4) ≥ 0
⇒ x ≤ - 4 or x ≥ 5
But -5 <x <4
∴ -5 < x < 4
Hence, function f(x) increases in domain x ∈ (-5, -4)
Case II :- x > 4
Then f'(x) ≥ ≥ 0 implies
6x2 - 6x - 36 ≥ 0
⇒ x2 - x - 6 ≥ 0
⇒ (x - 3) (x + 2) ≥ 0
⇒ x ≤ - 2 or x ≥ 3
But x > 4
Hence, f(x) increases in (4, ∞ )
From both cases, we can say that f(x) is increases in (-5, -4) U (4, ∞ ).
A = {x|x ∈ (-5, -4) U (4, ∞ )}
Top Questions on Functions
- If \( y = \operatorname{sgn}(\sin x) + \operatorname{sgn}(\cos x) + \operatorname{sgn}(\tan x) + \operatorname{sgn}(\cot x) \), where \(\operatorname{sgn}(p)\) denotes the signum function of \(p\), then the sum of elements in the range of \(y\) is:
- Statement 1 : The function \(f:\mathbb{R}\to\mathbb{R}\) defined by \[ f(x)=\frac{x}{1+|x|} \] is one–one.
Statement 2 : The function \(f:\mathbb{R}\to\mathbb{R}\) defined by \[ f(x)=\frac{x^2+4x-30}{x^2-8x+18} \] is many–one.
Which of the following is correct? - If domain of \(f(x) = \sin^{-1}\left(\frac{5-x}{2x+3}\right) + \frac{1}{\log_{e}(10-x)}\) is \((-\infty, \alpha] \cup (\beta, \gamma) - \{\delta\}\) then value of \(6(\alpha + \beta + \gamma + \delta)\) is equal to :
- Assertion (A): Let \( A = \{ x \in \mathbb{R} : -1 \leq x \leq 1 \} \). If \( f : A \to A \) be defined as \( f(x) = x^2 \), then \( f \) is not an onto function.
Reason (R): If \( y = -1 \in A \), then \( x = \pm \sqrt{-1} \notin A \). - If $ f(x) = 2x^2 - 3x + 5 $, find $ f(3) $.
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
If a random variable \( x \) has the probability distribution

then \( P(3<x \leq 6) \) is equal to- JEE Main - 2026
- Conditional Probability
Assuming in forward bias condition there is a voltage drop of \(0.7\) V across a silicon diode, the current through diode \(D_1\) in the circuit shown is ________ mA. (Assume all diodes in the given circuit are identical)

- JEE Main - 2026
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- Three small identical bubbles of water having same charge on each coalesce to form a bigger bubble. Then the ratio of the potentials on one initial bubble and that on the resultant bigger bubble is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electrostatics
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Compound (X), shown below, dissolves in \( NaHCO_3 \) solution and has two chiral carbon atoms.
Statement II : Compound (Y), shown below, has two carbons with \( sp^3 \) hybridization, one carbon with \( sp^2 \) and one carbon with \( sp \) hybridization.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- If the sum of the first four terms of an A.P. is \(6\) and the sum of its first six terms is \(4\), then the sum of its first twelve terms is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Arithmetic Progression
Concepts Used:
Functions
A function is a relation between a set of inputs and a set of permissible outputs with the property that each input is related to exactly one output. Let A & B be any two non-empty sets, mapping from A to B will be a function only when every element in set A has one end only one image in set B.
Kinds of Functions
The different types of functions are -
One to One Function: When elements of set A have a separate component of set B, we can determine that it is a one-to-one function. Besides, you can also call it injective.
Many to One Function: As the name suggests, here more than two elements in set A are mapped with one element in set B.
Moreover, if it happens that all the elements in set B have pre-images in set A, it is called an onto function or surjective function.
Also, if a function is both one-to-one and onto function, it is known as a bijective. This means, that all the elements of A are mapped with separate elements in B, and A holds a pre-image of elements of B.
Read More: Relations and Functions