In van der Wall equation
\([P=\frac{a}{V^2}[v-b]=RT;\)
P is pressure, V is volume, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature. The ratio of constants a/b is dimensionally equal to:
In van der Wall equation
\([P=\frac{a}{V^2}[v-b]=RT;\)
P is pressure, V is volume, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature. The ratio of constants a/b is dimensionally equal to:
- \(\frac{P}{V}\)
- \(\frac{V}{P}\)
- PV
- PV3
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The correct otpion is(C): PV
From the equation
[a] ≡ [PV2] [b] ≡ [V]
\(⇒[\frac{a}{b}]≡[PV]\)
Top Questions on Ideal gas equation
- What is the ideal gas law equation?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Ideal gas equation
- Which of the following gases is most likely to deviate from ideal gas behavior at high pressures and low temperatures?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Ideal gas equation
- A sample of gas occupies 10 L at 300 K and 2 atm. What will be its volume at 400 K and 1 atm?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Ideal gas equation
- What is the molar volume of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP)?
- VITEEE - 2025
- Chemistry
- Ideal gas equation
- A gas occupies 2 liters at a pressure of 3 atm. What will be its volume when the pressure is reduced to 1.5 atm at constant temperature?
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Ideal gas equation
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
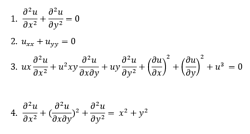
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
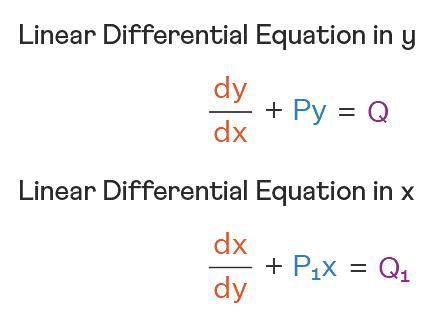
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations