Five charges +q, +5q, –2q, +3q and –4q are situated as shown in the figure. The electric flux due to this configuration through the surface S is


- \( \frac{5q}{\epsilon_0} \)
- \( \frac{4q}{\epsilon_0} \)
- \( \frac{3q}{\epsilon_0} \)
- \( \frac{q}{\epsilon_0} \)
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
To find the electric flux through the surface \( S \) due to the given configuration of charges, we apply Gauss's Law. Gauss's Law states that the total electric flux \( \Phi_E \) through a closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed \( Q_{\text{enc}} \) divided by the permittivity of free space \( \epsilon_0 \):
\(\Phi_E = \frac{Q_{\text{enc}}}{\epsilon_0}\)
In this problem, you have five charges: +q, +5q, –2q, +3q, and –4q. It is given that the surface \( S \) encloses the charges +q, +5q, and –2q. Let's calculate the net charge within the surface:
- Charge +q
- Charge +5q
- Charge –2q
So, the total enclosed charge \( Q_{\text{enc}} \) is:
\(Q_{\text{enc}} = q + 5q - 2q = 4q\)
Substitute this back into Gauss's Law:
\(\Phi_E = \frac{4q}{\epsilon_0}\)
Hence, the electric flux through the surface \( S \) is \(\frac{4q}{\epsilon_0}\).
The correct answer is the option: \(\frac{4q}{\epsilon_0}\).
Approach Solution -2
According to Gauss’s law, the electric flux Φ through a closed surface is given by:
\(Φ = \frac{q_{in}}{\epsilon_0}\),
where qin is the total charge enclosed by the surface.
In this problem, the charges enclosed by the surface are \(q_{in} = q + (-2q) + 5q = 4q\).
Thus, the electric flux is:
\(Φ = \frac{4q}{\epsilon_0}\).
The correct answer is Option (2).
Top Questions on Electric Flux
A line charge of length \( \frac{a}{2} \) is kept at the center of an edge BC of a cube ABCDEFGH having edge length \( a \). If the density of the line is \( \lambda C \) per unit length, then the total electric flux through all the faces of the cube will be : (Take \( \varepsilon_0 \) as the free space permittivity)

- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- An electric field \( \vec{E} \) is given by:
\[ \vec{E} = \begin{cases} +100\, \hat{i} \dfrac{\text{N}}{\text{C}} & \text{for } x>0 \\ -100\, \hat{i} \dfrac{\text{N}}{\text{C}} & \text{for } x<0 \end{cases} \] A right circular cylinder of length \( 10\, \text{cm} \) and radius \( 2\, \text{cm} \), is placed such that its axis coincides with the x-axis and its two faces are at \( x = -5\, \text{cm} \) and \( x = 5\, \text{cm} \). Calculate: (a) the net outward flux through the cylinder, and (b) the net charge inside the cylinder.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- The angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in a transverse wave is (except when the particle passes through the mean position)
- KCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
A metallic sphere of radius \( R \) carrying a charge \( q \) is kept at a certain distance from another metallic sphere of radius \( R_4 \) carrying a charge \( Q \). What is the electric flux at any point inside the metallic sphere of radius \( R \) due to the sphere of radius \( R_4 \)?

- KCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Flux
- A charge is kept at the central point P of a cylindrical region. The two edges subtend a half-angle \(\theta\) at P, as shown in the figure. When \(\theta = 30\) , then the electric flux through the curved surface of the cylinder is \(Φ\). If \(\theta= 60\degree\) , then the electric flux through the curved surface becomes \(Φ/√𝑛\), where the value of n is______.
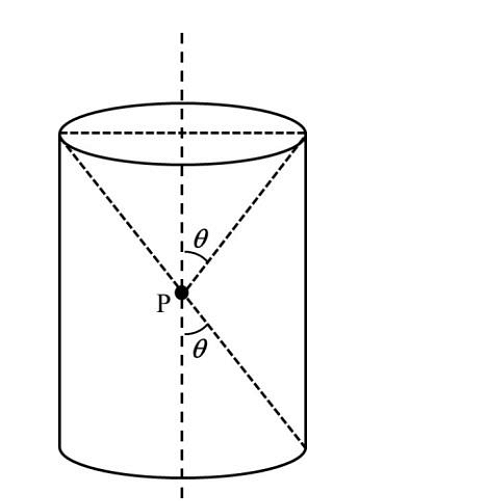
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Flux
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry