Amongst the following, the number of oxide(s) which are paramagnetic in nature is
Na2O, KO2, NO2, N2O, ClO2, NO, SO2, Cl2O
Na2O, KO2, NO2, N2O, ClO2, NO, SO2, Cl2O
Correct Answer: 4
Solution and Explanation
To determine the number of paramagnetic oxides among the listed compounds, we need to understand the concept of paramagnetism, which arises due to the presence of unpaired electrons in a molecule.
Analysis of each oxide:
- Na2O: Sodium oxide is a simple ionic compound with O2− ions having no unpaired electrons. Diamagnetic.
- KO2: Potassium superoxide contains the O2− ion, which has one unpaired electron. Paramagnetic.
- NO2: Nitrogen dioxide has an unpaired electron. Paramagnetic.
- N2O: Nitrous oxide has no unpaired electrons in its bonding structure. Diamagnetic.
- ClO2: Chlorine dioxide has an odd number of valence electrons, resulting in unpaired electrons. Paramagnetic.
- NO: Nitric oxide has one unpaired electron. Paramagnetic.
- SO2: Sulfur dioxide has paired electrons in its structure. Diamagnetic.
- Cl2O: Dichlorine monoxide does not have unpaired electrons. Diamagnetic.
Conclusion: The oxides that are paramagnetic are KO2, NO2, ClO2, and NO. Thus, the number of paramagnetic oxides is 4, which is within the given range (4,4).
Top Questions on Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Phenol can be distinguished from propanol by using the reagent
- KCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Calculate the potential for half-cell containing 0.01 M K\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\)(aq), 0.01 M Cr\(^{3+}\)(aq), and 1.0 x 10\(^{-4}\) M H\(^+\)(aq).
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Number of isomeric products formed by monochlorination Of \(2-methyl \) \(butane\) in presence of sunlight is
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Find out the final product C

- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Moles of \(CH_4\) required for formation of \(22\) \(g\) of \(CO_2\) is \(m \times 10^{-2}\) The value of \(m\) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The moment of inertia of a square loop made of four uniform solid cylinders, each having radius R and length L (\(R \le L\)) about an axis passing through the mid points of opposite sides, is (Take the mass of the entire loop as M) :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Kinematics
Which of the following best represents the temperature versus heat supplied graph for water, in the range of \(-20^\circ\text{C}\) to \(120^\circ\text{C}\)?

- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- When a part of a straight capillary tube is placed vertically in a liquid, the liquid rises upto certain height \( h \). If the inner radius of the capillary tube, density of the liquid and surface tension of the liquid decrease by \(1%\) each, then the height of the liquid in the tube will change by ________ %.
- JEE Main - 2026
- thermal properties of matter
- A gas of certain mass filled in a closed cylinder at a pressure of $3.23\,\text{kPa}$ has temperature $50^\circ$C. The gas is now heated to double its temperature. The modified pressure is ___ Pa.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- Let the circle \(x^2+y^2=4\) intersect the \(x\)-axis at points \(A(a,0)\) and \(B(b,0)\). Let \(P(2\cos\alpha,2\sin\alpha)\), \(0<\alpha<\frac{\pi}{2}\), and \(Q(2\cos\beta,2\sin\beta)\) be two points on the circle such that \((\alpha-\beta)=\frac{\pi}{2}\). Then the point of intersection of lines \(AQ\) and \(BP\) lies on:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Circles
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
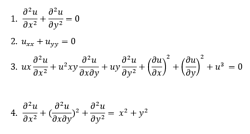
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
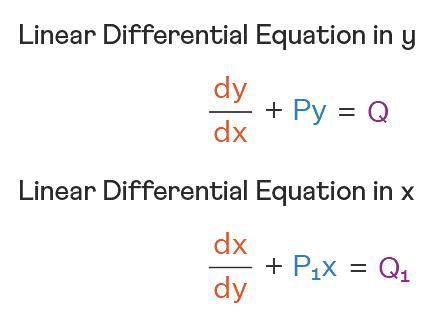
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations