A radioactive nuclei X decays simultaneously to two nuclei Y and Z as:
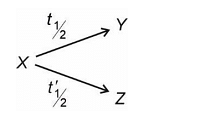
t½ is 12 minutes while t'½ is 3 minutes. Find the time in which nuclei X decays 50%.

t½ is 12 minutes while t'½ is 3 minutes. Find the time in which nuclei X decays 50%.
4.8 minutes
15 minutes
2.4 minutes
9 minutes
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is 2.4 minutes
Top Questions on Radioactivity
- The half-life of radioactive isotope Zn$^{65}$ is 245 days. Find the time after which activity of Zn sample remains 75% of its initial value.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Radioactivity
- The half-life of a radioactive substance is 4 hours. If initially there are 256 grams, how much remains after 10 hours?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Physics
- Radioactivity
- Write two properties of beta rays.
- Bihar Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Radioactivity
- The half-life of a radioactive element is 10 minutes. Find the time in which its activity reduces to 1/16 of the original.
- The half life of a radioactive substance is 10 minutes. If $n_1$ and $n_2$ are the number of atoms decayed in 20 and 30 minutes respectively, then $n_1 : n_2 = $
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Physics
- Radioactivity
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Concepts Used:
Radioactivity
Radioactivity is a phenomenon observed in certain elements where unstable atomic nuclei spontaneously emit energy and subatomic particles. This process is driven by the desire of the nucleus to achieve a more stable state. It's crucial to understand the three main types of radioactive decay:
Alpha Decay: In alpha decay, a nucleus emits an alpha particle, consisting of two protons and two neutrons.
Beta Decay: Beta decay involves the emission of a beta particle, which can be a positron or an electron, from an unstable nucleus.
Gamma Decay: Gamma decay releases gamma rays, electromagnetic radiation, to achieve a more stable nuclear state.
The emission of these particles and energy is a result of nuclear instability. The rate of decay is characterized by the half-life, the time taken for half of the radioactive material to undergo decay. Radioactivity has diverse applications, from medical treatments and industrial processes to power generation in nuclear reactors.