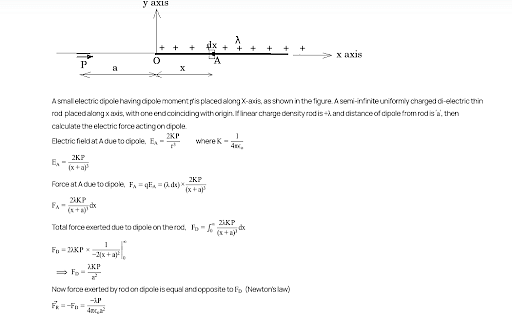
A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move ?
- towards the left as its potential energy will increase.
- towards the right as its potential energy will decrease.
- towards the left as its potential energy will decrease.
- towards the right as its potential energy will increase.
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The given problem involves a dipole placed in an electric field. To determine the direction in which the dipole will move, we need to consider the behavior of a dipole in an electric field.
When a dipole is placed in an electric field, the dipole experiences a torque that tends to align it with the field. The potential energy of the dipole in an electric field is given by:
U = -p · E
Where:
- p is the dipole moment vector,
- E is the electric field vector,
- U is the potential energy.
The dipole will move towards the direction where its potential energy decreases. This happens when the dipole rotates to align with the electric field, minimizing its potential energy.
In this case, as the dipole aligns with the electric field, it moves towards the right, where the potential energy is lower.
Final Answer:
The dipole will move towards the right as its potential energy will decrease.
Top Questions on Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of dipole moment \( \vec{p} = (0.8\,\hat{i} + 0.6\,\hat{j}) \times 10^{-29}\,\text{Cm} \) is placed in an electric field \( \vec{E} = 1.0 \times 10^7\,\hat{k}\,\text{V/m} \). Calculate the magnitude of the torque acting on it and the angle it makes with the x-axis, at this instant.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of mass \( m \), charge \( q \), and length \( l \) is placed in a uniform electric field \( E = E_0 \hat{i} \). When the dipole is rotated slightly from its equilibrium position and released, the time period of its oscillations will be:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of dipole moment \(6 \times 10^{-6} \) Cm is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude \(10^6\) V/m. Initially, the dipole moment is parallel to the electric field. The work that needs to be done on the dipole to make its dipole moment opposite to the field will be ________________________ J.
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of dipole moment \( \vec{p} \) consists of point charges \( +q \) and \( -q \), separated by distance \( 2a \). Derive an expression for the electric potential in terms of its dipole moment at a point at a distance \( x \, (x \gg a) \) from its centre and lying:
(I) along its axis, and
(II) along its bisector (equatorial) line.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
Charges are uniformly spread on the surface of a conducting sphere. The electric field from the center of the sphere in a point outside the sphere varies with distance \( r \) from the center as

- KCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges -q and q, separated by a distance of 2a. The direction from q to -q is said to be the direction in space.
p=q×2a
where,
p denotes the electric dipole moment, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Force Applied on Electric Dipole