Which of the following helps in the transport of fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane?
- Acyl carrier protein
- Carnitine
- Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
- Carnitine and albumin
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
In biochemistry, the transport of fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane is a crucial step in fatty acid oxidation. This process is facilitated by the compound carnitine. Carnitine acts as a carrier molecule that transports activated fatty acids from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix, where they undergo β-oxidation to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Here is the process by which carnitine functions:
- Activation of fatty acids: Before transportation, fatty acids are activated in the cytosol to form acyl-CoA by the enzyme acyl-CoA synthetase.
- Formation of acyl-carnitine: The acyl group from the acyl-CoA is transferred to carnitine by the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase I, located on the outer mitochondrial membrane. This forms acyl-carnitine.
- Transport across the membrane: The acyl-carnitine is then transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane by a translocase enzyme.
- Regeneration of acyl-CoA: Inside the mitochondrial matrix, another enzyme, carnitine acyltransferase II, transfers the acyl group back to CoA to form acyl-CoA, which enters β-oxidation, while free carnitine is recycled back to the cytosol.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is carnitine, as it is the molecule responsible for transferring long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria where they can be broken down for energy.
Top Questions on Lipids
- A patient presents with xanthomas on the Achilles tendon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A patient with multiple tendon xanthomas is found to have a serum cholesterol level of 398 mg/dL and an LDL level of 220 mg/dL. What is the most likely defect?
- Which of the following has the lowest melting point?
- Ceramides are
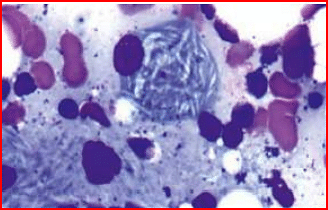
- A child presents with bone pain and hepatosplenomegaly. A trephine biopsy and aspirate show the following finding. Which of the following is the most likely enzyme deficient in this condition?
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science