Question:
A patient with multiple tendon xanthomas is found to have a serum cholesterol level of 398 mg/dL and an LDL level of 220 mg/dL. What is the most likely defect?
A patient with multiple tendon xanthomas is found to have a serum cholesterol level of 398 mg/dL and an LDL level of 220 mg/dL. What is the most likely defect?
Show Hint
In cases of familial hypercholesterolemia, look for tendon xanthomas and significantly elevated LDL levels. The defect usually lies in the LDL receptor.
Updated On: Jul 9, 2025
- Lipoprotein lipase deficiency
- LDL receptor defect
- Defective Apo B-100
- PCSK9 gain-of-function mutation
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
In biochemistry, multiple tendon xanthomas and elevated serum cholesterol and LDL levels are indicative of familial hypercholesterolemia. This condition is commonly caused by a defect in the LDL receptor. Let's break down why this is the most likely defect:
- Lipoprotein lipase deficiency: This condition leads to hypertriglyceridemia, not hypercholesterolemia. It would result in elevated chylomicrons and VLDL rather than LDL.
- LDL receptor defect: This is the most common cause of familial hypercholesterolemia. It results in elevated LDL levels because LDL particles can't be taken up by the liver effectively, hence the buildup in the bloodstream.
- Defective Apo B-100: While this could also cause elevated LDL, it typically presents less severely than an LDL receptor defect and is less common.
- PCSK9 gain-of-function mutation: This would increase LDL levels but is less common than an LDL receptor defect. Plus, the presence of tendon xanthomas strongly points toward familial hypercholesterolemia due to an LDL receptor defect.
Given these considerations, the LDL receptor defect is the most likely cause of the observed symptoms in this patient.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Lipids
- A patient presents with xanthomas on the Achilles tendon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Which of the following has the lowest melting point?
- Ceramides are
- A child presents with bone pain and hepatosplenomegaly. A trephine biopsy and aspirate show the following finding. Which of the following is the most likely enzyme deficient in this condition?
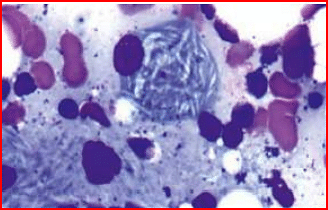
- A child presents with mental retardation, bone pain, and inability to walk. On funduscopic examination, a cherry red spot is seen. There is no organomegaly. What is the most likely diagnosis?
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
View More Questions