Two nucleotides are joined together by a linkage known as:
Disulphide linkage
Glycosidic linkage
Phosphodiester linkage
Peptide linkage
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
To determine the correct linkage that joins two nucleotides, we need to understand the structure of nucleotides and how they connect to form nucleic acids like DNA or RNA.
- Nucleotide Structure:
- A nucleotide consists of three components: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- Linkage Between Nucleotides:
- Nucleotides are joined in a strand by bonding through the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3' -OH group of the sugar in the next nucleotide. This bonding creates a long chain, with a backbone made of sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate and so on.
- The specific type of bond forming this linkage is known as a phosphodiester linkage. In a phosphodiester bond, the phosphate group links the 5' carbon of one sugar to the 3' carbon of the next sugar in the chain.
- This phosphodiester linkage is crucial for creating the backbone structure of nucleic acids, allowing them to assume the correct geometry and function.
- Ruling Out Other Options:
- Disulphide linkage: Typically found in protein structures, particularly in the stabilization of protein tertiary and quaternary structures, and not in nucleic acids.
- Glycosidic linkage: Common in carbohydrates, linking sugars by connecting an anomeric carbon of a sugar to another molecule, such as forming part of nucleoside structure, not between nucleotides.
- Peptide linkage: Found in proteins, forming the backbone of proteins by linking amino acids, not nucleotides.
Thus, the correct answer is that two nucleotides are joined together by a phosphodiester linkage.
Top Questions on Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides are joined together by:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Nucleic Acids
- Assertion (A): Uracil base is present in DNA. Reason (R): DNA undergoes self-replication.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2024
- Chemistry
- Nucleic Acids
- Identify the polarity from ‘X’ to ‘Y’ in the mRNA segment shown. Mention how many more amino acids can be added to the polypeptide that is being translated and why.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2024
- Biology
- Nucleic Acids
- Given below are two statements:
I. Cytosine and guanine are formed in equal quantities in DNA hydrolysis.
II. Adenine and uracil are formed in equal quantities in RNA hydrolysis. The correct answer is:- AP EAPCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- Nucleic Acids
- Uracil is a base present in RNA with the following structure $\%$ of $N$ in uracil is ___
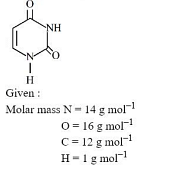
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Nucleic Acids
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The system of linear equations
$x + y + z = 6$
$2x + 5y + az = 36$
$x + 2y + 3z = b$
has- JEE Main - 2026
- Matrices and Determinants
- The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with time period \(T\) is expressed as \[ x(t)=A\sin\omega t, \] where \(A\) is the amplitude of oscillation. If the maximum value of the potential energy of the oscillator is found at \[ t=\frac{T}{2\beta}, \] then the value of \(\beta\) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Waves and Oscillations
- A complex number 'z' satisfy both \(|z-6|=5\) & \(|z+2-6i|=5\) simultaneously. Find the value of \(z^3 + 3z^2 - 15z + 141\).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Algebra
In the given figure, the blocks $A$, $B$ and $C$ weigh $4\,\text{kg}$, $6\,\text{kg}$ and $8\,\text{kg}$ respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surfaces is $0.5$. The force $\vec{F}$ required to slide the block $C$ with constant speed is ___ N.
(Given: $g = 10\,\text{m s}^{-2}$)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational Mechanics
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational motion
Concepts Used:
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are explained as long-chain polymeric molecules, where the monomer (the repeating unit) is referred to as the nucleotides. Thus many times nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides. The two main kinds of nucleic acids are-
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Chemically, DNA is a composition of a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid, and some cyclic bases that have nitrogen in them. DNA has β-D-2-deoxyribose in it, in the form of the sugar moiety.
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
The RNA molecule is a composition of phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and some cyclic bases containing nitrogen. The sugar moiety inside RNA molecules is β-D-ribose.