The reaction of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene with hydrazine produces a yellow orange solid X used for the identification of an organic functional group G. X and G, respectively, are
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
To solve this question, we need to determine the products of the reaction between 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene and hydrazine.
Step 1: Understanding the Reaction
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene is a compound with strong electron-withdrawing nitro groups at the 2 and 4 positions on a benzene ring, which activates the fluorine for nucleophilic substitution.
Upon reaction with hydrazine (NH2NH2), the nucleophilic nitrogen on the hydrazine attacks the carbon with the fluorine, displacing the fluoride ion. This reaction is characteristic and leads to the formation of a hydrazone linkage.
Step 2: Identifying the Yellow Orange Solid X
The product of this reaction is known to be a 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone, a yellow-orange solid. This compound, referred to as X in the question, is known for its intense coloration, which is used in chemical analysis.
Step 3: Determining the Functional Group G
The functional group that 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone helps identify is the carbonyl group (C=O), commonly found in aldehydes and ketones. This is because hydrazone derivatives form selectively when carbonyl compounds react with hydrazine derivatives.
In the context of this reaction, hydrazines are typical reagents for testing carbonyl functionalities, and the formation of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone derivatives confirms the presence of such a group.
Conclusion
Thus, the compounds X and G are identified as 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone and carbonyl group, respectively.

Top Questions on Qualitative Organic Analysis
- The major products X and Y in the following reactions
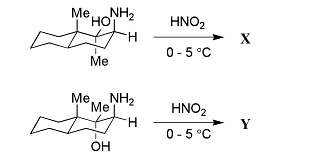
respectively, are- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Organic Chemistry
- Qualitative Organic Analysis
- An alkaline (NaOH) solution of a compound produces a yellow colored solution on addition of NaBO3. The compound is
- IIT JAM CY - 2023
- Organic Chemistry
- Qualitative Organic Analysis
- An organic compound having molecular formula $C_9H_{10}O_2$ exhibits the following spectral characteristics:
$'H NMR: \delta 9.72 (t, 1H), 7.1 (d, 2H), 6.7 (d, 2H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 3.6 (d, 2H)$
$IR: ~1720 cm^{-1}$
The most probable structure of the compound is- IIT JAM CY - 2022
- Organic Chemistry
- Qualitative Organic Analysis
The compound(s) that shows(show) positive haloform test is(are)

- IIT JAM CY - 2018
- Organic Chemistry
- Qualitative Organic Analysis
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- Among the following, the correct condition(s) for spontaneity is(are)
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas starting from state A, goes through B and C to state D, as shown in the figure. Total change in entropy (in J K\(^{-1}\)) during this process is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
The number of chiral carbon centers in the following molecule is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
- Consider the following matrices A and B.
\[ A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 7 \\ 0 & 0 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B = \begin{pmatrix} 10 & 11 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 12 & 13 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 15 & 16 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 17 & 18 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
If \( C = AB \), the sum of the diagonal elements of \( C \) is ..............
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
A tube fitted with a semipermeable membrane is dipped into 0.001 M NaCl solution at 300 K as shown in the figure. Assume density of the solvent and solution are the same. At equilibrium, the height of the liquid column \( h \) (in cm) is .........

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry


