The area of the region given by A={(x,y); \(x^2\)≤y≤min{x+2,4−3x}} is
\(\frac{31}{8}\)
\(\frac{17}{6}\)
\(\frac{19}{6}\)
\(\frac{27}{8}\)
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
A = {(x, y) : x2 ≤ y ≤ min {x + 2, 4 – 3x}
So, the area of the required region
A=\(\int_{-1}^{\frac{1}{2}}\)(x+2−x2)dx+\(\int_{1}^{\frac{1}{2}}\)(4−3x−x2)dx
=[\(\frac{x^2}{2}+2x-\frac{x^3}{3}\)]\(^{\frac{1}{2}}\)-1+[4x−\(\frac{3x^2}{2}\)−\(\frac{x^3}{3}\)]\(^{\frac{1}{2}}\)1
=(\(\frac{1}{8}\)+1−\(\frac{1}{24}\))−(\(\frac{1}{2}\)−2+\(\frac{1}{3}\))+(4−\(\frac{3}{2}\)−\(\frac{1}{3}\))−(2−\(\frac{3}{8}\)−\(\frac{1}{24}\))=\(\frac{17}{6}\)
Top Questions on Area between Two Curves
- Let $A_1$ be the bounded area enclosed by the curves $y=x^2+2$, $x+y=8$ and $y$-axis that lies in the first quadrant. Let $A_2$ be the bounded area enclosed by the curves $y=x^2+2$, $y^2=x$, $x=2$ and $y$-axis that lies in the first quadrant. Then $A_1-A_2$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Area between Two Curves
- If the area of the region $ \{(x, y) : 1 + x^2 \leq y \leq \min(x + 7, 11 - 3x)\} $ is $ A $, then $ 3A $ is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Area between Two Curves
If the area of the region $\{ (x, y) : |x - 5| \leq y \leq 4\sqrt{x} \}$ is $A$, then $3A$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Area between Two Curves
- The area of the region bounded by the curve $ y = \max\{|x|, |x-2|\} $, then x-axis and the lines x = -2 and x = 4 is equal to ____.
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Area between Two Curves
- If the area of the region bounded by the curves $ y = 4 - \frac{x^2}{4} $ and $ y = \frac{x - 4}{2} $ is equal to $ \alpha $, then $ 6\alpha $ equals:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Area between Two Curves
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Approximations
The theory that is part of mathematics is the approximation theory. An approximation is employed when it becomes difficult to seek out the exact value of any number. It is also essential to round off the errors resulting in approximation.
Symbol of Approximation:
In general, the wavy equal “≈” sign is used to represent the approximate values that stand for “almost equal to”.
For Example ⇢ π ≈ 3.14
Approximations of Derivatives:
Consider y = f(x) = any function of x.
Let,
Δx = the small change in x
Δy = the corresponding change in y
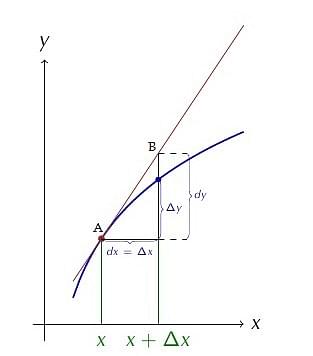
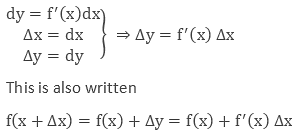
Here are some of the essential points that are required to be remembered:
- The differential of the dependent variable can not be equal to the increase of the variable whereas the differential of the independent variable can be equal to the increase of the variable.
- Absolute error in x is the change Δx.