The angle between two diagonals of a cube is
Show Hint
The angle between any pair of diagonals can be shown to be Cosθ=1/3.
- $30^\circ$
- $45^\circ$
- $\cos^{-1} \left(\frac{1}{3} \right)$
- $\cos^{-1} \left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)$
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
The correct answer is Option C) \(\cos^{-1} \left(\frac{1}{3} \right)\)

O(0, 0, 0), A(a, 0, 0), B(0, a, 0), R(0, 0, a), D(a, a, 0), K(a, 0, a), L(0, a, a,), P(a, a, a) direction-cosines of diagonal Op is proportional to (a, a, a)
so, Op's direct cosines are:

The angle between two diagonals of a cube is cos–11/3.
Discover More Topics From This Chapter: Three-Dimensional Geometry
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is Option C) \(\cos^{-1} \left(\frac{1}{3} \right)\)
Real Life Applications
- The angle between the diagonals was employed in the design of the Millennium Bridge in London and Burj Khalifa to guarantee that the structure would be sturdy and wouldn't swing excessively in the wind.
- It is also used in the design of some types of trusses to guarantee that the truss is sturdy and won't collapse under load.
Question can also be asked as
- What is the angle between any two diagonals of a cube?
- What is the smallest angle between any two diagonals of a cube?
- How to find the angle between two diagonals of a cube?
- What is the formula for the angle between two diagonals of a cube?
- How to prove that the angle between two diagonals of a cube is 90 degrees?
- What is the acute angle between two diagonals of a cube?
- What is the dihedral angle between two diagonals of a cube?
- What is the angle between the two main diagonals of a cube?
- What is the angle between the two space diagonals of a cube?
Approach Solution -3
The correct answer is Option C) \(\cos^{-1} \left(\frac{1}{3} \right)\)
DC’s of diagonals OP and AQ are
1/√3,1/√3,1/√3and−1/√3,1/√3,1/√3
So, cos θ=(1/√3)(−1/√3)+(1/√3)(1/√3)+(1/√3)(1/√3)
=1/3
so, θ = cos–1 (1/3).
Diagonal of a Cube Formula
The Diagonal of a Cube Formula can be denoted by:
The diagonal of a Cube = \(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{3}x\end{array}\)
The primary diagonal of a Cube cuts through the center of the Cube; the diagonal of the Cube's face is not the main diagonal. The main diagonal of a cube can be determined by the help of multiplying the length of one side with the square root of 3 (it is also called the body diagonal of a cube).
Also Read:
Top Questions on Three Dimensional Geometry
- If the distances of the point \( (1,2,a) \) from the line \[ \frac{x-1}{1}=\frac{y}{2}=\frac{z-1}{1} \] along the lines \[ L_1:\ \frac{x-1}{3}=\frac{y-2}{4}=\frac{z-a}{b} \quad \text{and} \quad L_2:\ \frac{x-1}{1}=\frac{y-2}{4}=\frac{z-a}{c} \] are equal, then \( a+b+c \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- The value of the integral \( \int_{\frac{\pi}{24}}^{\frac{5\pi}{24}} \frac{dx}{1 + \sqrt[3]{\tan 2x}} \) is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
Let the lines $L_1 : \vec r = \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k + \lambda(2\hat i + 3\hat j + 4\hat k)$, $\lambda \in \mathbb{R}$ and $L_2 : \vec r = (4\hat i + \hat j) + \mu(5\hat i + + 2\hat j + \hat k)$, $\mu \in \mathbb{R}$ intersect at the point $R$. Let $P$ and $Q$ be the points lying on lines $L_1$ and $L_2$, respectively, such that $|PR|=\sqrt{29}$ and $|PQ|=\sqrt{\frac{47}{3}}$. If the point $P$ lies in the first octant, then $27(QR)^2$ is equal to}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let a line $L$ passing through the point $P(1,1,1)$ be perpendicular to the lines \[ \frac{x-4}{4}=\frac{y-1}{1}=\frac{z-1}{1} \quad \text{and} \quad \frac{x-17}{1}=\frac{y-71}{1}=\frac{z}{0}. \] Let the line $L$ intersect the $yz$-plane at the point $Q$.
Another line parallel to $L$ and passing through the point $S(1,0,-1)$ intersects the $yz$-plane at the point $R$.
Then the square of the area of the parallelogram $PQRS$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let \( L \) be the line \[ \frac{x+1}{2} = \frac{y+1}{3} = \frac{z+3}{6} \] and let \( S \) be the set of all points \( (a,b,c) \) on \( L \), whose distance from the line \[ \frac{x+1}{2} = \frac{y+1}{3} = \frac{z-9}{0} \] along the line \( L \) is \( 7 \). Then \[ \sum_{(a,b,c)\in S} (a+b+c) \] is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Three Dimensional Geometry
Mathematically, Geometry is one of the most important topics. The concepts of Geometry are derived w.r.t. the planes. So, Geometry is divided into three major categories based on its dimensions which are one-dimensional geometry, two-dimensional geometry, and three-dimensional geometry.
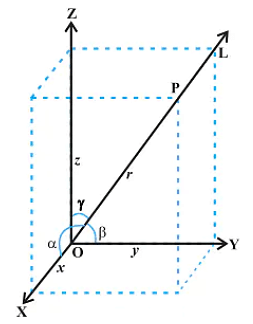
Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios of Line:
Consider a line L that is passing through the three-dimensional plane. Now, x,y and z are the axes of the plane and α,β, and γ are the three angles the line makes with these axes. These are commonly known as the direction angles of the plane. So, appropriately, we can say that cosα, cosβ, and cosγ are the direction cosines of the given line L.