Question:
Resistance of each side is $R$. Find equivalent resistance between two opposite points as shown in the figure.

Resistance of each side is $R$. Find equivalent resistance between two opposite points as shown in the figure. 
Show Hint
In symmetric resistor networks, identify equipotential points to reduce the circuit easily.
Updated On: Jan 28, 2026
- $\dfrac{4}{5}R$
- $\dfrac{8}{5}R$
- $\dfrac{8}{10}R$
- $\dfrac{2}{5}R$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Use symmetry of the network.
The hexagonal resistor network is symmetric about the line joining the opposite points. Hence, current divides equally in equivalent branches.
Step 2: Simplification of the internal connections.
Each diagonal divides resistance $R$ into two equal parts of $R/2$. These resistances can be combined using series and parallel rules.
Step 3: Equivalent resistance of the inner triangle.
\[ R_{\text{inner}} = \dfrac{R \times R}{R + R} = \dfrac{R}{2} \]
Step 4: Combining inner and outer resistances.
The reduced network gives two resistances $2R$ and $\dfrac{4R}{3}$ in parallel.
Step 5: Final equivalent resistance.
\[ R_{\text{eq}} = \dfrac{2R \times \dfrac{4R}{3}}{2R + \dfrac{4R}{3}} = \dfrac{8R^2}{10R} = \dfrac{4}{5}R \]
The hexagonal resistor network is symmetric about the line joining the opposite points. Hence, current divides equally in equivalent branches.
Step 2: Simplification of the internal connections.
Each diagonal divides resistance $R$ into two equal parts of $R/2$. These resistances can be combined using series and parallel rules.
Step 3: Equivalent resistance of the inner triangle.
\[ R_{\text{inner}} = \dfrac{R \times R}{R + R} = \dfrac{R}{2} \]
Step 4: Combining inner and outer resistances.
The reduced network gives two resistances $2R$ and $\dfrac{4R}{3}$ in parallel.
Step 5: Final equivalent resistance.
\[ R_{\text{eq}} = \dfrac{2R \times \dfrac{4R}{3}}{2R + \dfrac{4R}{3}} = \dfrac{8R^2}{10R} = \dfrac{4}{5}R \]
Was this answer helpful?
2
1
Top Questions on Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Electric field in a region is given by \[ \vec{E} = A x\,\hat{i} + B y\,\hat{j}, \] where \( A = 10 \,\text{V/m}^2 \) and \( B = 5 \,\text{V/m}^2 \). If the electric potential at a point \( (10, 20) \) is \(500\ \text{V}\), then the electric potential at origin is __________ V.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- If a particle of mass 10 mg and charge 2 µC at rest is subjected to a uniform electric field of potential difference 160 V, then the velocity acquired by the particle is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A charge of 10 coulomb is brought from infinity to a point \( P \) near a charged body and in this process 200 joules of work is done. Electric potential at point \( P \) is:
- JEECUP - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points C and P (in V) shown in the figure is:
(Take \(\frac{1}{4}\pi\epsilon_0 = 9 × 109\)\(\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}=9\times10^9\) SI units)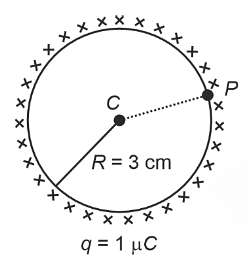
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Two point charges \( 20 \, \mu C \) and \( -10 \, \mu C \) are separated by a distance of 1 m in air. At what point on the line joining the two charges, the electric potential is zero.
- COMEDK UGET - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
View More Questions