Let \(P1:\overrightarrow{r}.(2\^i+\^j−3\^k )=4\) be a plane. Let \(P_2\) be another plane which passes through points \((2, - 3, 2)\), \((2, - 2, -3)\) and \((1, -4, 2)\). If the direction ratios of the line of intersection of \(P_1\) and \(P_2\) be \(16, α,β,\) then the value of \(α + β\) is equal to _____ .
Correct Answer: 28
Solution and Explanation
Direction ratio of normal to \(P_1≡< 2, 1, – 3 >\)
and \(P2≡\begin{vmatrix} \hat i & \hat j & \hat k \\[0.3em] 0 & 1 & -5 \\[0.3em] -1 & -2 & 5 \end{vmatrix}\)
\(P_2=−5\hat i−\hat j(−5)+\hat k(1)\)
i.e.\(< –5, 5, 1 >\)
d.r’s of line of intersection are along vector
\(\begin{vmatrix} \hat i & \hat j & \hat k \\[0.3em] 2 & 1 & -3 \\[0.3em] -5 & 5 & 1 \end{vmatrix}\)\(=\hat i(16)−\hat j(−13)+\hat k(15)\)
i.e.\(< 16, 13, 15 >\)
Therefore, \(α + β = 13 + 15 = 28\)
So, the answer is \(28\).
Top Questions on Plane
- The distance between the two planes $2x + 3y + 4z = 4$ and $4x + 6y + 8z = 12$ is:
- If one of the lines given by \( 6x^2 - xy + 4cy^2 = 0 \) is \( 3x + 4y = 0 \), then \( c \) equals
- The equation of the plane passing through the point \( (1, 1, 1) \) and perpendicular to the planes \( 2x + y - 2z = 5 \) and \( 3x - 6y - 2z = 7 \) is:
- Let the foot of perpendicular from a point \( P(1,2,-1) \) to the straight line \( L : \frac{x}{1} = \frac{y}{0} = \frac{z}{-1} \) be \( N \). Let a line be drawn from \( P \) parallel to the plane \( x + y + 2z = 0 \) which meets \( L \) at point \( Q \). If \( \alpha \) is the acute angle between the lines \( PN \) and \( PQ \), then \( \cos \alpha \) is equal to:
- Let the acute angle bisector of the two planes \( x - 2y - 2z + 1 = 0 \) and \( 2x - 3y - 6z + 1 = 0 \) be the plane \( P \). Then which of the following points lies on \( P \)?
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Distance of a Point from a Plane
The shortest perpendicular distance from the point to the given plane is the distance between point and plane. In simple terms, the shortest distance from a point to a plane is the length of the perpendicular parallel to the normal vector dropped from the particular point to the particular plane. Let's see the formula for the distance between point and plane.
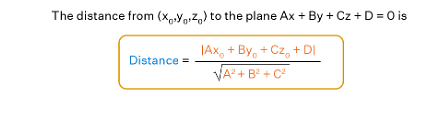
Read More: Distance Between Two Points