Leaching of gold with dilute aqueous solution of NaCN in presence of oxygen gives complex [A], which on reaction with zinc forms the elemental gold and another complex [B]. [A] and [B], respectively are :
- \([Au(CN)_4]^–\) and \([Zn(CN)_2 (OH)_2]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (OH)_4]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (CN)_4]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_4]^{2-}\) and \([Zn (CN)_6]^{4-}\)
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
In the metallurgy of gold
\(4Au + 8CN^– + 2H_2O + O_2 → 4[Au(CN)_2]^– + 4OH^–\)
\(2[Au(CN)_2]^– + Zn → [Zn(CN)_4]^{2–} + 2Au\)
So, the correct option is (C): \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (CN)_4]^{2-}\)
Top Questions on Concentration of ores
- Which of the following are carbonate ores?
I. Siderite
II. Kaolinite
III. Calamine
IV. Sphalerite- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Identify the sulphide ore among the following:
- TS POLYCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Which of the following methods is used for the concentration of ore?
- TS POLYCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Pyrolusite ore is:
- BCECE Nursing - 2024
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- A → P is a zero-order reaction. At 298 K, the rate constant of the reaction is \( 1 \times 10^{-3} \) mol L\(^{-1}\) s\(^{-1}\). Initial concentration of 'A' is 0.1 mol L\(^{-1}\). What is the concentration of 'A' after 10 sec?
- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
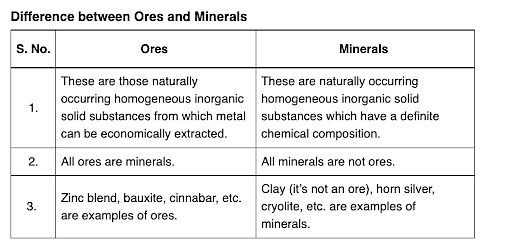
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal