In \(Δ\)PQR, right angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
Solution and Explanation
Given that,
PR + QR = 25
PQ = 5 Let PR be x.
Therefore, QR = 25 - x

Applying Pythagoras theorem in \(Δ\)PQR, we obtain
\(\text{PR}^ 2 = \text{PQ}^ 2 + \text{QR}^ 2 \)
\(x^2= (5)^ 2 + (25 - x)^ 2 \)
\(x^2= 25 + 625 + x^ 2 - 50x \)
\(50x=650\)
\(x=13\)
Therefore, PR = 13 cm
QR = (25 - 13) cm = 12 cm
\(\text{sin p} =\frac{\text{ Opposite Side}}{\text{Hypotenuse }}= \frac{QR}{PR} = \frac{12}{13}\)
\(\text{sin p} = \frac{\text{Opposite Side}}{\text{Hypotenuse }}= \frac{QR}{PR} =\frac{ 12}{13}\)
\(\text{tan p} =\frac{\text{Opposite Side}}{\text{Adjacent side }}= \frac{QR}{PQ} = \frac{12}{5}\)
Top Questions on Trigonometric Ratios
If $\tan \theta = \tfrac{3}{4}$, then the value of $\cos \theta$ will be:
- UP Board X - 2025
- Mathematics
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Evaluate \( \dfrac{2 \tan 30^\circ}{1 + \tan^2 30^\circ} \)
- AP POLYCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Trigonometric Ratios
- If \( 15 \cot A = 8 \), then \( \sin A = \, ? \)
- AP POLYCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Evaluate \( (\sec A + \tan A)(1 - \sin A) = \ ? \)
- AP POLYCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Which of the following is true?
- AP POLYCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Trigonometric Ratios
Questions Asked in CBSE X exam
- Find 'mean' and 'mode' of the following data : Frequency Distribution Table
Class 0 – 15 15 – 30 30 – 45 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 Frequency 11 8 15 7 10 9 - CBSE Class X - 2025
- Statistics
Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Plant Biology
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit:
(i) Commercial Bank
(ii) Landlords
(iii) Government
(iv) Money Lende- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Concepts Used:
Trigonometric Functions
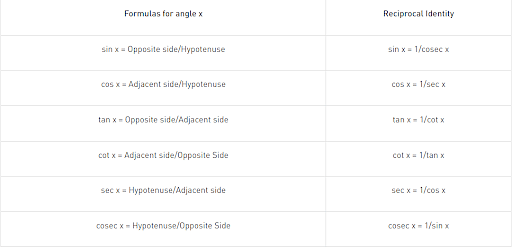
The relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angle triangle is described by trigonometry functions, sometimes known as circular functions. These trigonometric functions derive the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle. In trigonometry, there are three primary functions of sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan). The other three main functions can be derived from the primary functions as cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cosec).
Six Basic Trigonometric Functions:
- Sine Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
sin x = a/h
- Cosine Function: The ratio between the length of the adjacent side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
cos x = b/h
- Tangent Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the adjacent side length.
tan x = a/b
Tan x can also be represented as sin x/cos x
- Secant Function: The reciprocal of the cosine function.
sec x = 1/cosx = h/b
- Cosecant Function: The reciprocal of the sine function.
cosec x = 1/sinx = h/a
- Cotangent Function: The reciprocal of the tangent function.
cot x = 1/tan x = b/a
Formulas of Trigonometric Functions: