If the orthocentre of the triangle, whose vertices are $(1,2),(2,3)$ and $(3,1)$ is $(\alpha, \beta)$, then the quadratic equation whose roots are $\alpha+4 \beta$ and $4 \alpha+\beta$, is
- $x^2-19 x+90=0$
- $x^2-20 x+99=0$
- $x^2-18 x+80=0$
- $x^2-22 x+120=0$
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
The correct answer is option (B) : x2−20x+99=0

\((\frac{β−3}{α−2})(\frac{1}{−2})=−1\)
\(β−3=2α−4\)
\(β=2α−1\)
\(m_{AH}\times m_{BC}=−1\)
\(⇒(\frac{β−2}{α−1})(−2)=−1\)
\(⇒2β−4=α−1\)
\(⇒2(2α−1)=α+3\)
\(⇒3α=5\)
\(α=\frac{5}{3}, β=\frac{7}{3} \)
\(⇒H(\frac{5}{3}, \frac{7}{3})\)
\(α+4β= \frac{5}{3} + \frac{28}{3} = \frac{33}{3} =11\)
\(β+4α= \frac{7}{3} + \frac{20}{3} = \frac{27}{3} = 9\)
\(x^2 −20x+99=0\)
Approach Solution -2
Step 1: Finding slopes of perpendicular altitudes: \[ m = \frac{-1}{2} = -\frac{1}{2} \] \[ \text{Here } m_{BH} \times m_{AC} = -1 \] \[ \beta - 3 = 2\alpha - 4 \] \[ \beta = 2\alpha - 1 \] Step 2: Using midpoint formula and relations, we find: \[ \alpha = \frac{5}{3}, \quad \beta = \frac{7}{3} \]
Step 3: Now, computing roots: \[ \alpha + 4\beta = 11, \quad 4\alpha + \beta = 9 \] \[ x^2 - (11 + 9)x + 11 \times 9 = 0 \] \[ x^2 - 20x + 99 = 0 \]
Top Questions on Definite Integral
- Evaluate the definite integral: \( \int_{-2}^{2} |x^2 - x - 2| \, dx \)
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Definite Integral
- For \( x \in \left( -\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \), if\[y(x) = \int \frac{\csc x + \sin x}{\csc x \sec x + \tan x \sin^2 x} \, dx\]and\[\lim_{x \to -\frac{\pi}{2}} y(x) = 0\]then \( y\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right) \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Definite Integral
- The value of the integral \[ \int_{-1}^{2} \log_e \left( x + \sqrt{x^2 + 1} \right) \, dx \] is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Definite Integral
The value \( 9 \int_{0}^{9} \left\lfloor \frac{10x}{x+1} \right\rfloor \, dx \), where \( \left\lfloor t \right\rfloor \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( t \), is ________.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Definite Integral
- The value of \(\lim_{{n \to \infty}} \sum_{{k=1}}^{n} \frac{n^3}{{(n^2 + k^2)(n^2 + 3k^2)}}\) is
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Definite Integral
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
- 10 mole of an ideal gas is undergoing the process shown in the figure. The heat involved in the process from \( P_1 \) to \( P_2 \) is \( \alpha \) Joule \((P_1 = 21.7 \text{ Pa}, P_2 = 30 \text{ Pa}, C_v = 21 \text{ J/K mol}, R = 8.3 \text{ J/mol K})\). The value of \( \alpha \) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- The system of linear equations
$x + y + z = 6$
$2x + 5y + az = 36$
$x + 2y + 3z = b$
has- JEE Main - 2026
- Matrices and Determinants
- The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with time period \(T\) is expressed as \[ x(t)=A\sin\omega t, \] where \(A\) is the amplitude of oscillation. If the maximum value of the potential energy of the oscillator is found at \[ t=\frac{T}{2\beta}, \] then the value of \(\beta\) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Waves and Oscillations
Concepts Used:
Definite Integral
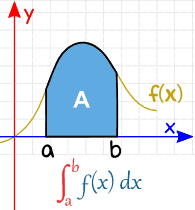
Definite integral is an operation on functions which approximates the sum of the values (of the function) weighted by the length (or measure) of the intervals for which the function takes that value.
Definite integrals - Important Formulae Handbook
A real valued function being evaluated (integrated) over the closed interval [a, b] is written as :
\(\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx\)
Definite integrals have a lot of applications. Its main application is that it is used to find out the area under the curve of a function, as shown below: