How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Electric field in a region is given by \[ \vec{E} = A x\,\hat{i} + B y\,\hat{j}, \] where \( A = 10 \,\text{V/m}^2 \) and \( B = 5 \,\text{V/m}^2 \). If the electric potential at a point \( (10, 20) \) is \(500\ \text{V}\), then the electric potential at origin is __________ V.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
Resistance of each side is $R$. Find equivalent resistance between two opposite points as shown in the figure.

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- If a particle of mass 10 mg and charge 2 µC at rest is subjected to a uniform electric field of potential difference 160 V, then the velocity acquired by the particle is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A charge of 10 coulomb is brought from infinity to a point \( P \) near a charged body and in this process 200 joules of work is done. Electric potential at point \( P \) is:
- JEECUP - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points C and P (in V) shown in the figure is:
(Take \(\frac{1}{4}\pi\epsilon_0 = 9 × 109\)\(\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}=9\times10^9\) SI units)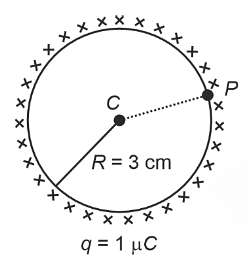
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
Questions Asked in CBSE X exam
- The sum of a number and its reciprocal is \(\frac{13}{6}\). Find the number.
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Quadratic Equations
- If the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by \( S_n = \frac{n}{2}(3n+1) \), then the first term of the A.P. is
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Arithmetic Progression
- Find 'mean' and 'mode' of the following data : Frequency Distribution Table
Class 0 – 15 15 – 30 30 – 45 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 Frequency 11 8 15 7 10 9 - CBSE Class X - 2025
- Statistics
Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Plant Biology
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Concepts Used:
Electric Potential
Electric potential, also known as voltage, is a scalar quantity that measures the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge in an electric field. It is denoted by the symbol V and is measured in volts (V).
The electric potential at a point in an electric field is defined as the amount of work done per unit charge to bring a positive test charge from infinity to that point. The electric potential at a point is also equal to the potential energy per unit charge of a positive test charge placed at that point.
Electric potential is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism and is used to describe the behavior of electric fields and charges. It is also used to calculate the electric potential difference, or voltage, between two points in an electric field.
The electric potential difference between two points is equal to the work done per unit charge to move a positive test charge from one point to the other. The electric potential difference is also equal to the product of the electric field strength and the distance between the two points.
Electric potential has many practical applications, such as in the design and operation of electrical circuits, electric motors, and generators. It is also used in electroplating, electrochemical cells, and other electrochemical processes. Understanding electric potential is crucial for the development and advancement of modern technology.