Given below are two statements.
Statement I : Electric potential is constant within and at the surface of each conductor.
Statement II : Electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor at every point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Statement I : Electric potential is constant within and at the surface of each conductor.
Statement II : Electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor at every point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
- Both statement I and statement II are correct
- Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
- Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
- Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Since, in the bulk of a conductor,
\(\vec E_{net}=0\)
Therefore, the potential would be constant.
\(⇒\) Statement I is correct.
Since a conductor’s surface is equipotential, \(\dot E\) just outside is perpendicular to the surface.
So, the correct option is (A): Both statement I and statement II are correct.
Top Questions on Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Electric field in a region is given by \[ \vec{E} = A x\,\hat{i} + B y\,\hat{j}, \] where \( A = 10 \,\text{V/m}^2 \) and \( B = 5 \,\text{V/m}^2 \). If the electric potential at a point \( (10, 20) \) is \(500\ \text{V}\), then the electric potential at origin is __________ V.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
Resistance of each side is $R$. Find equivalent resistance between two opposite points as shown in the figure.

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- If a particle of mass 10 mg and charge 2 µC at rest is subjected to a uniform electric field of potential difference 160 V, then the velocity acquired by the particle is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A charge of 10 coulomb is brought from infinity to a point \( P \) near a charged body and in this process 200 joules of work is done. Electric potential at point \( P \) is:
- JEECUP - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points C and P (in V) shown in the figure is:
(Take \(\frac{1}{4}\pi\epsilon_0 = 9 × 109\)\(\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}=9\times10^9\) SI units)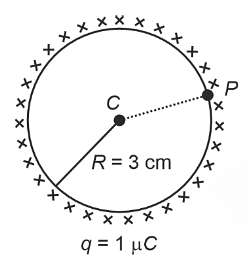
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A complex number 'z' satisfy both \(|z-6|=5\) & \(|z+2-6i|=5\) simultaneously. Find the value of \(z^3 + 3z^2 - 15z + 141\).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Algebra
In the given figure, the blocks $A$, $B$ and $C$ weigh $4\,\text{kg}$, $6\,\text{kg}$ and $8\,\text{kg}$ respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surfaces is $0.5$. The force $\vec{F}$ required to slide the block $C$ with constant speed is ___ N.
(Given: $g = 10\,\text{m s}^{-2}$)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational Mechanics
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational motion
- If \[ \frac{\tan(A-B)}{\tan A}+\frac{\sin^2 C}{\sin^2 A}=1, \quad A,B,C\in\left(0,\frac{\pi}{2}\right), \] then:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Trigonometry
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II for an isothermal process of an ideal gas system.

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics and Work Done
Concepts Used:
Electric Potential
Electric potential, also known as voltage, is a scalar quantity that measures the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge in an electric field. It is denoted by the symbol V and is measured in volts (V).
The electric potential at a point in an electric field is defined as the amount of work done per unit charge to bring a positive test charge from infinity to that point. The electric potential at a point is also equal to the potential energy per unit charge of a positive test charge placed at that point.
Electric potential is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism and is used to describe the behavior of electric fields and charges. It is also used to calculate the electric potential difference, or voltage, between two points in an electric field.
The electric potential difference between two points is equal to the work done per unit charge to move a positive test charge from one point to the other. The electric potential difference is also equal to the product of the electric field strength and the distance between the two points.
Electric potential has many practical applications, such as in the design and operation of electrical circuits, electric motors, and generators. It is also used in electroplating, electrochemical cells, and other electrochemical processes. Understanding electric potential is crucial for the development and advancement of modern technology.