Find the products formed if chlorine reacts with the cold and dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
Find the products formed if chlorine reacts with the cold and dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution and Explanation
When chlorine reacts with cold and dilute sodium hydroxide (\(NaOH\)) solution, the following products are formed:
Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl): Chlorine (\(Cl_2\)) reacts with sodium hydroxide (\(NaOH\)) to produce sodium hypochlorite (\(NaOCl\)) as one of the primary products. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
\(Cl_2 + 2NaOH → NaOCl + NaCl + H_2O \)
Sodium Chloride (NaCl): In addition to sodium hypochlorite, sodium chloride (\(NaCl\)) is also formed as a product. The balanced chemical equation shows the formation of sodium chloride:
\(Cl_2 + 2NaOH → NaOCl + NaCl + H_2O \)
Water (H2O): Water is produced as a byproduct of the reaction. The balanced chemical equation includes water as one of the products:
\(Cl_2 + 2NaOH → NaOCl + NaCl + H_2O\)
So, when chlorine reacts with a cold and dilute sodium hydroxide solution, the products formed are sodium hypochlorite (\(NaOCl\)), sodium chloride (\(NaCl\)), and water (\(H_2O\)).
Top Questions on Chemical Reactions
- One mole of Cl$_2$(g) was passed into 2 L of cold 2 M KOH solution. After the reaction, the concentrations of Cl$^-$, ClO$^-$ and OH$^-$ are respectively (assume volume remains constant)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions
The colour of the solution observed after about 1 hour of placing iron nails in copper sulphate solution is:
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Science
- Chemical Reactions
- Example of thermal decomposition reaction are:
- \( \text{2AgCl} \rightarrow \text{2Ag} + \text{Cl}_2 \)
- \( \text{CaCO}_3 \rightarrow \text{CaO} + \text{CO}_2 \)
- \( \text{2H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow \text{2H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \)
- \( \text{2KClO}_3 \rightarrow \text{2KCl} + \text{3O}_2 \)
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Science
- Chemical Reactions
- In which one of the following situations a chemical reaction does not occur?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Science
- Chemical Reactions
- The colour of the solution observed after about 1 hour of placing iron nails in copper sulphate solution is:
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Science
- Chemical Reactions
Questions Asked in AP EAMCET exam
Which of the following are ambident nucleophiles?
[A.] CN$^{\,-}$
[B.] CH$_{3}$COO$^{\,-}$
[C.] NO$_{2}^{\,-}$
[D.] CH$_{3}$O$^{\,-}$
[E.] NH$_{3}$- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
- The correct sequence of enzymes involved in the commercial production of ethanol by fermentation from sugar is:
- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
- At 298 K, the ionization constant of \( {CN}^- \) is \( 2.08 \times 10^{-6} \). What is the ionization constant of its conjugate acid? (Given \( K_w = 10^{-14} \))
- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
Identify the anomers from the following.

- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
The standard Gibbs free energy change \( \Delta G^\circ \) of a cell reaction is \(-301 { kJ/mol}\). What is \( E^\circ \) in volts?
(Given: \( F = 96500 { C/mol}\), \( n = 2 \))- AP EAMCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
Concepts Used:
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
Law of Chemical Equilibrium states that at a constant temperature, the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants each raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients as represented by the balanced chemical equation.
Let us consider a general reversible reaction;
A+B ↔ C+D
After some time, there is a reduction in reactants A and B and an accumulation of the products C and D. As a result, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of backward reaction increases.
Eventually, the two reactions occur at the same rate and a state of equilibrium is attained.
By applying the Law of Mass Action;
The rate of forward reaction;
Rf = Kf [A]a [B]b
The rate of backward reaction;
Rb = Kb [C]c [D]d
Where,
[A], [B], [C] and [D] are the concentrations of A, B, C and D at equilibrium respectively.
a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients of A, B, C and D respectively.
Kf and Kb are the rate constants of forward and backward reactions.
However, at equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
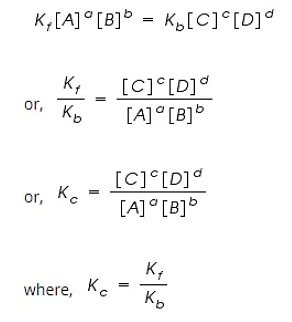
Kc is called the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations.
The above equation is known as the equation of Law of Chemical Equilibrium.