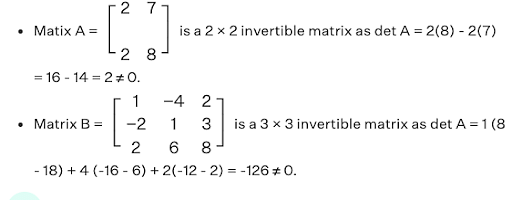Find the inverse of each of the matrices, if it exists. \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 \\ -4 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)
Solution and Explanation
Let A=\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 \\ -4 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)
We know that \(A = IA\)
\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 \\ -4 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)\(=A\)\(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 \\ 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)\(= A\)\(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\) \((C_1\rightarrow C_1+2C_2)\)
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)\(=A\)\(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\) \((C_2\rightarrow C_2+C_1)\)
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)\(=A\) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & \frac12 \\ 2 & \frac32 \end{bmatrix}\) \((C_2\rightarrow \frac{1}{2}C_2) \)
\(\therefore A^{-1}=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & \frac12 \\ 2 & \frac32 \end{bmatrix}\)
Top Questions on Matrices
- The number of $3\times2$ matrices $A$, which can be formed using the elements of the set $\{-2,-1,0,1,2\}$ such that the sum of all the diagonal elements of $A^{T}A$ is $5$, is
- If \[ X=\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{bmatrix} \] is a solution of the system of equations $AX=B$, where \[ \text{adj }A= \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 2 & 2\\ -5 & 0 & 5\\ 1 & -2 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B=\begin{bmatrix}4\\0\\2\end{bmatrix}, \] then $|x+y+z|$ is equal to
Let \[ f(x)=\int \frac{7x^{10}+9x^8}{(1+x^2+2x^9)^2}\,dx \] and $f(1)=\frac14$. Given that

- For the matrices \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \) and \( B = \begin{bmatrix} -29 & 49 \\ -13 & 18 \end{bmatrix} \), if \( (A^{15} + B) \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0\\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \), then among the following which one is true?}
- Let the relation \( R \) on the set \( M = \{1, 2, 3, \ldots, 16\} \) be given by \[ R = \{(x, y) : 4y = 5x - 3,\; x, y \in M\}. \] Then the minimum number of elements required to be added in \( R \), in order to make the relation symmetric, is equal to
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- Find the value of $x$, if \[ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 2 & 5 & 1 \\ 15 & 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ x \\ 2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \]
- Two point charges of \( -5\,\mu C \) and \( 2\,\mu C \) are located in free space at \( (-4\,\text{cm}, 0) \) and \( (6\,\text{cm}, 0) \) respectively.
(a) Calculate the amount of work done to separate the two charges at infinite distance.
(b) If this system of charges was initially kept in an electric field \[ \vec{E} = \frac{A}{r^2}, \text{ where } A = 8 \times 10^4\, \text{N}\,\text{C}^{-1}\,\text{m}^2, \] calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Electrostatics
- 4,000 shares of ₹ 10 each were forfeited for non-payment of second and final call money of ₹ 2 per share. The minimum amount that the company must collect at the time of reissue of these shares will be :
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Accounting for Share Capital
- If $y = a \cos(\log x) + b \sin(\log x)$, then $x^2y'' + xy'1$ is:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Continuity and differentiability

A ladder of fixed length \( h \) is to be placed along the wall such that it is free to move along the height of the wall.
Based upon the above information, answer the following questions:(iii) (b) If the foot of the ladder, whose length is 5 m, is being pulled towards the wall such that the rate of decrease of distance \( y \) is \( 2 \, \text{m/s} \), then at what rate is the height on the wall \( x \) increasing when the foot of the ladder is 3 m away from the wall?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Application of derivatives
Concepts Used:
Invertible matrices
A matrix for which matrix inversion operation exists, given that it satisfies the requisite conditions is known as an invertible matrix. Any given square matrix A of order n × n is called invertible if and only if there exists, another n × n square matrix B such that, AB = BA = In, where In is an identity matrix of order n × n.
For example,
It can be observed that the determinant of the following matrices is non-zero.