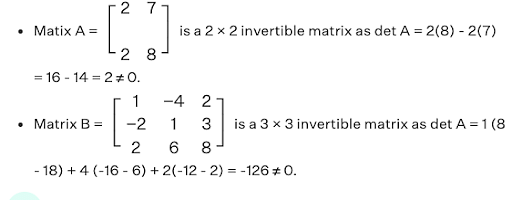Find the inverse of each of the matrices, if it exists.
\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 10\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)
\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 10\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)
Solution and Explanation
Let A=\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 10\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)
We know that \(A = IA \)
\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 10\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0\\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}\)A
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1\\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}\)A \((R_1\rightarrow R_1-R_2)\)
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3\\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1\\ -2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\) A \((R_2\rightarrow R_2-2R_2)\)
⇒ \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0\\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 7 & -10\\ -2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\)\(A\)et \((R_1\rightarrow R_1-3R_2)\)
\(\therefore A^{-1}=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} 7 & -10\\ -2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\)
Top Questions on Matrices
- The number of $3\times2$ matrices $A$, which can be formed using the elements of the set $\{-2,-1,0,1,2\}$ such that the sum of all the diagonal elements of $A^{T}A$ is $5$, is
- If \[ X=\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{bmatrix} \] is a solution of the system of equations $AX=B$, where \[ \text{adj }A= \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 2 & 2\\ -5 & 0 & 5\\ 1 & -2 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B=\begin{bmatrix}4\\0\\2\end{bmatrix}, \] then $|x+y+z|$ is equal to
Let \[ f(x)=\int \frac{7x^{10}+9x^8}{(1+x^2+2x^9)^2}\,dx \] and $f(1)=\frac14$. Given that

- For the matrices \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \) and \( B = \begin{bmatrix} -29 & 49 \\ -13 & 18 \end{bmatrix} \), if \( (A^{15} + B) \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0\\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \), then among the following which one is true?}
- Let the relation \( R \) on the set \( M = \{1, 2, 3, \ldots, 16\} \) be given by \[ R = \{(x, y) : 4y = 5x - 3,\; x, y \in M\}. \] Then the minimum number of elements required to be added in \( R \), in order to make the relation symmetric, is equal to
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- (a) Briefly explain Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
(b) Four metals with their work functions are listed below:
K = 2.3 eV, Na = 2.75 eV, Mo = 4.17 eV, Ni = 5.15 eV.
The radiation of wavelength 330 nm from a laser source placed 1 m away, falls on these metals.
Which of these metals will not show photoelectric emission?
What will happen if the laser source is brought closer to a distance of 50 cm?- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Photoelectric Effect
- Differentiate $2\cos^2 x$ w.r.t. $\cos^2 x$.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Derivatives
- The diagonals of a parallelogram are given by \( \mathbf{a} = 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \) and \( \mathbf{b} = \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - \hat{k}\) . Find the area of the parallelogram.
- Altima Ltd. invited applications for 2,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 at a premium of ₹ 4 per share. Amount payable:
On application and allotment – ₹ 7 (incl. ₹ 1 premium)
On first and final call – Balance.
Applications received for 2,40,000 shares. 30,000 rejected. Manvi allotted 4,000 shares failed to pay first and final call. Her shares were forfeited. These were reissued at ₹ 4 per share fully paid-up.
Pass journal entries in the books of Altima Ltd.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Accounting for Share Capital
- Which of the following options shows the correct chronological order of events related to Indian National Movement?
I. Second Round Table Conference
II. Peasant Movement in Bardoli
III. Champaran Satyagraha
IV. Jallianwala Bagh Massacre- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Indian Freedom Movement
Concepts Used:
Invertible matrices
A matrix for which matrix inversion operation exists, given that it satisfies the requisite conditions is known as an invertible matrix. Any given square matrix A of order n × n is called invertible if and only if there exists, another n × n square matrix B such that, AB = BA = In, where In is an identity matrix of order n × n.
For example,
It can be observed that the determinant of the following matrices is non-zero.