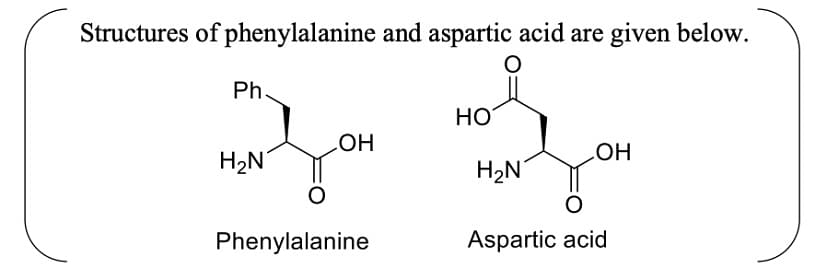
Aspartame, an artificial sweetener, is a dipeptide aspartyl phenylalanine methyl ester. The structure of aspartame is

The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
Step 1: Understanding Aspartame
Aspartame is a dipeptide formed by the condensation of aspartic acid and phenylalanine. The methyl ester group is added to the carboxyl group of the phenylalanine residue.
Step 2: Structural Features of Aspartame
- Peptide bond: Formed between the carboxyl group of aspartic acid and the amino group of phenylalanine.
- Methyl ester group: Attached to the terminal carboxyl group of phenylalanine.
Step 3: Verifying the Structure
Structure (B) correctly shows the peptide bond between aspartic acid and phenylalanine, with the methyl ester group on phenylalanine.
Conclusion
The correct structure of aspartame is represented by option (B).
Approach Solution -2
To solve the problem, we need to determine the correct structure of aspartame, which is a dipeptide consisting of aspartyl phenylalanine methyl ester.
1. Understanding the Components:
Aspartame is made from aspartic acid and phenylalanine, with the phenylalanine part esterified as a methyl ester.
- Aspartic acid has two carboxyl groups, one of which forms a peptide bond.
- Phenylalanine contains a phenyl (Ph) group attached to the alpha carbon.
2. Structure of Aspartame:
- The amino group of phenylalanine bonds with the carboxyl group of aspartic acid.
- The free carboxyl group of phenylalanine is converted to methyl ester (–COOCH₃).
- The resulting structure is a dipeptide: aspartyl-phenylalanine methyl ester.
3. Identifying the Correct Option:
Among the given options, option (B) correctly shows:
- Aspartic acid with free amino and carboxyl groups.
- Phenylalanine linked via peptide bond.
- Methyl ester group at the carboxyl terminal of phenylalanine.
Thus, option (B) is the correct structure of aspartame.
Final Answer:
Option (B)
Top Questions on Biomolecules
In the given pentapeptide, find out an essential amino acid (\(Y\)) and the sequence present in the pentapeptide.

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Given below are two statements for the following reaction sequence:

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- The correct trend in the first ionization enthalpies of the elements in the 3rd period of periodic table is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Match List-I with List-II.

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- The correct statements are :
A. Activation energy for enzyme catalysed hydrolysis of sucrose is lower than that of acid catalysed hydrolysis.
B. During denaturation, secondary and tertiary structures of a protein are destroyed but primary structure remains intact.
C. Nucleotides are joined together by glycosidic linkage between \( C_1 \) and \( C_4 \) carbons of the pentose sugar.
D. Quaternary structure of proteins represents overall folding of the polypeptide chain.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
Monocyclic compounds $ P, Q, R $ and $ S $ are the major products formed in the reaction sequences given below.
The product having the highest number of unsaturated carbon atom(s) is:
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Organic Chemistry
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties




