A tower stands at the center of a circular park. and are two points on the boundary of the park such that subtends an angle of at the foot of the tower and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from or is . The height of the tower is
Show Hint

- \(\frac{2a}{ \sqrt{3} }\)
- \(2a\sqrt 3\)
- \(\frac {a}{\sqrt 3}\)
- \(a\sqrt 3\)
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Let be the tower at the centre of the circular park.
and are two points on the boundary of the park () subtends an angle of at the foot of the tower and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from or is
Let '' be the height of the tower.
We have to find the value of ''.

is an equilateral triangle.
Now in ,
[Using trigonometric ratios ]
The height of the tower is
Hence, the correct option is (C): \(\frac {a}{\sqrt 3}\).
Top Questions on Some Applications of Trigonometry
- If \[ \frac{\cos^2 48^\circ - \sin^2 12^\circ}{\sin^2 24^\circ - \sin^2 6^\circ} = \frac{\alpha + \sqrt{5\beta}}{2} \] then the value of \( (\alpha + \beta) \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The number of values of \( x \) satisfying \( \tan^{-1}(4x) + \tan^{-1}(6x) = \frac{\pi}{6} \) and \( x<\left[ \frac{-1}{2\sqrt{6}} , \frac{1}{2\sqrt{6}} \right] \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The number of solutions of the equation \( \tan 3x = \cot x \) in \( x \in [0, 2\pi] \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The minimum value of \( (\sin^{-1} x)^2 + (\cos^{-1} x)^2 \) in \( x \in \left[ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right] \) is \( \frac{a \pi^2}{b} \), then \( a + b \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The value of cosec10° - √3 sec10°
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
Concepts Used:
Trigonometric Functions
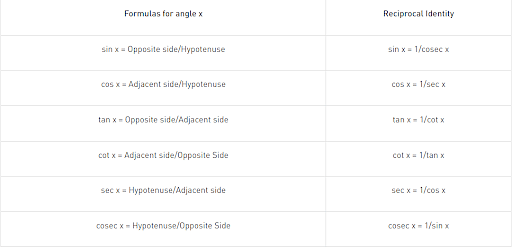
The relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angle triangle is described by trigonometry functions, sometimes known as circular functions. These trigonometric functions derive the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle. In trigonometry, there are three primary functions of sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan). The other three main functions can be derived from the primary functions as cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cosec).
Six Basic Trigonometric Functions:
- Sine Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
sin x = a/h
- Cosine Function: The ratio between the length of the adjacent side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
cos x = b/h
- Tangent Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the adjacent side length.
tan x = a/b
Tan x can also be represented as sin x/cos x
- Secant Function: The reciprocal of the cosine function.
sec x = 1/cosx = h/b
- Cosecant Function: The reciprocal of the sine function.
cosec x = 1/sinx = h/a
- Cotangent Function: The reciprocal of the tangent function.
cot x = 1/tan x = b/a
Formulas of Trigonometric Functions: