A student needs to prepare a buffer solution of propanoic acid and its sodium salt with pH 4. The ratio of
\(\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH] }\)
required to make buffer is _____.
Given : Ka(CH3CH2COOH) = 1.3 × 10–5
A student needs to prepare a buffer solution of propanoic acid and its sodium salt with pH 4. The ratio of
\(\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH] }\)
required to make buffer is _____.
Given : Ka(CH3CH2COOH) = 1.3 × 10–5
0.03
0.13
0.23
0.33
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is (B) : 0.13
\(CH_3CH_2COOH⇌CH_3CH_2COO^−+H^+\)
From Henderson equation
\(pH=pK_a+log\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}\)
\(4=−log 1.3×10^{−5} log\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}\)
\(−log^{10^{−4}}=−log1.3×10^{−5}+log\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}\)
\(−log^{10^{−4}}=−log1.3×10^{−5} \frac{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}{[CH_3CH_2COO^-]}\)
\(10^{−4}=1.3×10^{−5}\frac{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}{[CH_3CH_2COO^-]}\)
\(\frac{[CH_3CH_2COO^−]}{[CH_3CH_2COOH]}=0.13\)
Top Questions on Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Consider the following gaseous equilibrium in a closed container of volume $V$ at temperature $T$:
P$_2$(g) + Q$_2$(g) $\rightleftharpoons$ 2PQ(g)
Initially, 2 moles each of P$_2$(g), Q$_2$(g) and PQ(g) are present at equilibrium. One mole each of P$_2$ and Q$_2$ are added. The number of moles of P$_2$, Q$_2$ and PQ at the new equilibrium respectively are
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- $X_2(g) + Y_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2Z(g)$. Equilibrium moles of $X_2, Y_2, Z$ are 3, 3, 9 mol (in 1 L). 10 mol of Z(g) is added. New equilibrium moles of Z(g) is ___. (Nearest integer)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Observe the following equilibrium in a 1 L flask:
A(g) <=> B(g)
At temperature T (in K), the equilibrium concentrations of A and B are 0.5 M and 0.375 M respectively.
Then 0.1 moles of A is added into the flask and the system is heated to temperature T again to re-establish equilibrium.
The new equilibrium concentrations (in M) of A and B respectively are:- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- The plot of \(\log_{10}K\) vs \(\frac{1}{T}\) gives a straight line. The intercept and slope respectively are (where \(K\) is equilibrium constant).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- For the reaction \( \mathrm{A \rightleftharpoons B} \), the number of moles of A and B at equilibrium in a \(1\,\text{L}\) vessel are \(0.50\) and \(0.375\), respectively. If \(0.10\) mol of A is added further, determine the number of moles of A and B at the new equilibrium.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
Law of Chemical Equilibrium states that at a constant temperature, the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants each raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients as represented by the balanced chemical equation.
Let us consider a general reversible reaction;
A+B ↔ C+D
After some time, there is a reduction in reactants A and B and an accumulation of the products C and D. As a result, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of backward reaction increases.
Eventually, the two reactions occur at the same rate and a state of equilibrium is attained.
By applying the Law of Mass Action;
The rate of forward reaction;
Rf = Kf [A]a [B]b
The rate of backward reaction;
Rb = Kb [C]c [D]d
Where,
[A], [B], [C] and [D] are the concentrations of A, B, C and D at equilibrium respectively.
a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients of A, B, C and D respectively.
Kf and Kb are the rate constants of forward and backward reactions.
However, at equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
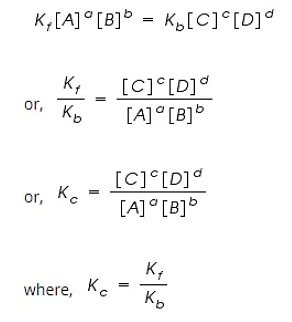
Kc is called the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations.
The above equation is known as the equation of Law of Chemical Equilibrium.