A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30 cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is________ mm.
Correct Answer: 225
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is: 225

1st refraction:
\(\frac{1.5}{V_1}-0=\frac{0.5}{15}\)
\(⇒ v_1 = 45 \)cm
2nd refraction:
\(\frac{1}{v_2}-\frac{1.5}{15}=\frac{-0.5}{-15}\)
\(⇒ \frac{1}{v_2}=\frac{1}{30}+\frac{1}{10}\)
\(⇒ v2 = +7.5 \)cm
\(⇒\) Distance from centre = 22.5 cm
Top Questions on Units and measurement
- Four persons measure the length of a rod as 20.00 cm, 19.75 cm, 17.01 cm and 18.25 cm. The relative error in the measurement of average length of the rod is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Units and measurement
- When both jaws of a vernier calipers touch each other, zero mark of the vernier scale is right to the zero mark of main scale. 4th mark on vernier scale coincides with a certain mark on the main scale. While measuring the length of a cylinder, observer observes 15 divisions on main scale and 5th division of vernier scale coincides with a main scale division. Measured length of cylinder is ________ mm. (Least count of Vernier calliper = \(0.1\) mm)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Units and measurement
- Two cars $A$ and $B$ each of mass $10^3$ kg are moving on parallel tracks separated by a distance of $10$ m, in same direction with speeds $72$ km/h and $36$ km/h. The magnitude of angular momentum of car $A$ with respect to car $B$ is _________ J.s.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Units and measurement
- Match the column

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Units and measurement
- Time period of a spring-block system is given by \(T = 2\pi\sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}\). If mass of the block is given by \(m = 10\,\text{g} \pm 10\,\text{mg}\) and time period is measured using a stopwatch having least count of \(2\,\text{s}\) and was found to be \(60\,\text{s}\) for \(50\) oscillations, then find the % error in measurement of \(k\).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Units and measurement
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
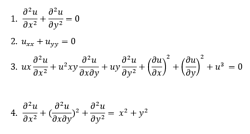
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
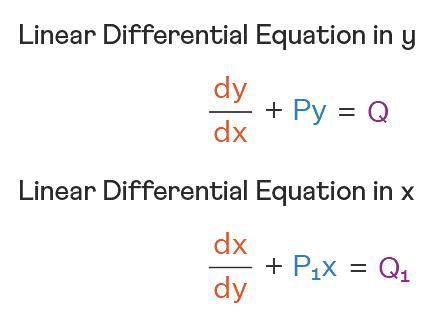
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations