A Combination of two charges +1 nC and -1 nC are separated by a distance of 1 μm. This Constituted electric dipole is placed in an electric field of 1000 V/m at an angle of 45 degree. The torque and the potential energy on the electric dipole are:
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) x10-12 N.m and \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) x10-12 J
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) x10-12 N.m and \(\sqrt{2}\) x10-12 J
\(\sqrt{2}\) x10-12 N.m and \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) x10-12 J
\(\sqrt{2}\) x10-12 N.m and \(\sqrt{2}\) x10-12 J
\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) x10-12 N.m and \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)x10-12 J
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
Given parameters:
- Charges: \( q = ±1 \, \text{nC} = ±10^{-9} \, \text{C} \)
- Separation: \( d = 1 \, \mu\text{m} = 10^{-6} \, \text{m} \)
- Electric field: \( E = 1000 \, \text{V/m} \)
- Angle: \( θ = 45° \)
Dipole moment calculation: \[ p = q \times d = 10^{-9} \times 10^{-6} = 10^{-15} \, \text{C.m} \]
Torque on dipole: \[ \tau = pE \sinθ = 10^{-15} \times 1000 \times \sin45° = \frac{10^{-12}}{\sqrt{2}} \, \text{N.m} \]
Potential energy: \[ U = -pE \cosθ = -10^{-15} \times 1000 \times \cos45° = -\frac{10^{-12}}{\sqrt{2}} \, \text{J} \]
Thus, the correct option is (A): \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \times 10^{-12} \, \text{N.m} \) and \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \times 10^{-12} \, \text{J} \).
Approach Solution -2
1. Calculate the dipole moment (p):
The electric dipole moment (p) is given by:
\[p = qd\]
where:
- q = 1 nC = 1 × 10⁻⁹ C (magnitude of charge)
- d = 1 μm = 1 × 10⁻⁶ m (separation between charges)
\[p = (1 \times 10^{-9} \, C)(1 \times 10^{-6} \, m) = 1 \times 10^{-15} \, C \cdot m\]
2. Calculate the torque (τ):
The torque (τ) on an electric dipole in an electric field (E) is given by:
\[\tau = pE\sin\theta\]
where θ = 45° is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
\[\tau = (1 \times 10^{-15} \, C \cdot m)(1000 \, V/m)\sin(45^\circ) = 10^{-12} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \, N \cdot m\]
3. Calculate the potential energy (U):
The potential energy (U) of an electric dipole in an electric field is given by:
\[U = -pE\cos\theta\]
\[U = -(1 \times 10^{-15} \, C \cdot m)(1000 \, V/m)\cos(45^\circ) = -10^{-12} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \, J\]
The question asks for the potential *energy*, so we're interested in the magnitude:
\[|U| = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \times 10^{-12} \, J\]
Top Questions on electrostatic potential and capacitance
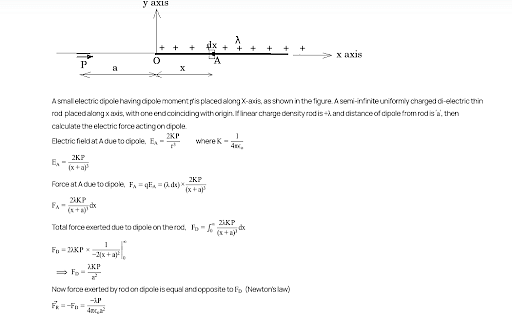
Find work done in bringing charge q = 3nC from infinity to point A as shown in the figure :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- A ray of light is incident on a refracting face AB of a prism ABC at an angle of \( 45^\circ \). The ray emerges from face AC and the angle of deviation is \( 15^\circ \). The angle of prism is \( 30^\circ \). Show that the emergent ray is normal to the face AC from which it emerges out. Find the refraction index of the material of the prism.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
Two capacitors \( C_1 \) and \( C_2 \) are connected in parallel to a battery. Charge-time graph is shown below for the two capacitors. The energy stored with them are \( U_1 \) and \( U_2 \), respectively. Which of the given statements is true?

- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Choke coil is simply a coil having a large inductance but a small resistance. Choke coils are used with fluorescent mercury-tube fittings. If household electric power is directly connected to a mercury tube, the tube will be damaged.
Reason (R): By using the choke coil, the voltage across the tube is reduced by a factor \( \frac{R}{\sqrt{R^2 + \omega^2 L^2}} \), where \( \omega \) is the frequency of the supply across resistor \( R \) and inductor \( L \). If the choke coil were not used, the voltage across the resistor would be the same as the applied voltage.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- Three infinitely long wires with linear charge density \( \lambda \) are placed along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis respectively. Which of the following denotes an equipotential surface?
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
Questions Asked in KEAM exam
- Which among the following has the highest molar elevation constant?
- KEAM - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- The formula of Ammonium phosphomolybdate is
- KEAM - 2025
- coordination compounds
- Which is a Lewis acid?
- KEAM - 2025
- Acids and Bases
- Hardness of water is estimated by titration with
- KEAM - 2025
- Solutions
- Which of the following gases has the lowest solubility in water at 298 K?
- KEAM - 2025
- Solutions
Concepts Used:
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges -q and q, separated by a distance of 2a. The direction from q to -q is said to be the direction in space.
p=q×2a
where,
p denotes the electric dipole moment, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Force Applied on Electric Dipole