20 mL of 0.02 M K2Cr2O7 solution is used for the titration of 10 mL of Fe2+ solution in the acidic medium. The molarity of Fe2+ solution is ______×10–2 M. (Nearest integer)
Correct Answer: 24
Approach Solution - 1
The titration equation for the reaction between dichromate ions (Cr2O72–) and iron ions (Fe2+) in an acidic medium is:
Cr2O72– + 6Fe2+ + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7H2O
The stoichiometry indicates that 1 mole of Cr2O72– oxidizes 6 moles of Fe2+.
Calculate moles of K2Cr2O7:
moles = Molarity × Volume (L) = 0.02 M × 0.020 L = 0.0004 mol
Since 1 mole of Cr2O72– reacts with 6 moles of Fe2+, moles of Fe2+ are:
6 × 0.0004 mol = 0.0024 mol
The molarity of Fe2+ solution is calculated using its volume:
Molarity = (moles/Volume in L) = 0.0024 mol / 0.010 L = 0.24 M
Express it as: 24 × 10–2 M.
The solution value is 24, which lies within the expected range (24,24). Thus, the molarity of the Fe2+ solution is 24×10–2 M.
Approach Solution -2
Applying the law of equivalence,
milliequivalents of Fe2+ = milliequivalents of K2Cr2O7
10 × 1 × M = 20 × 6 × .02
M = 24 × 10–2 M
∴ Answer will be 24.
Top Questions on Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Phenol can be distinguished from propanol by using the reagent
- KCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Calculate the potential for half-cell containing 0.01 M K\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\)(aq), 0.01 M Cr\(^{3+}\)(aq), and 1.0 x 10\(^{-4}\) M H\(^+\)(aq).
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Number of isomeric products formed by monochlorination Of \(2-methyl \) \(butane\) in presence of sunlight is
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Find out the final product C

- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Moles of \(CH_4\) required for formation of \(22\) \(g\) of \(CO_2\) is \(m \times 10^{-2}\) The value of \(m\) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
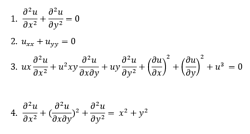
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
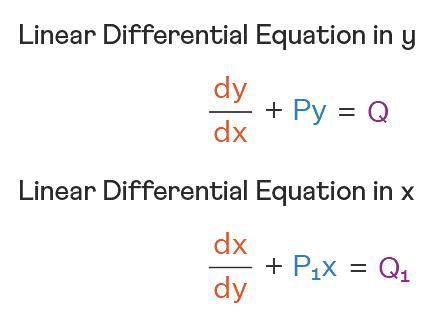
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations