Which one or more of the following statements is/are correct regarding the electromotive force generated by the electron transfer chain?
Show Hint
- ( It is used for the synthesis of ATP. )
- ( It is not used for active transport processes. )
- ( It includes a pH gradient component. )
- ( It does not include an electrical potential gradient component. )
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Analysis of Each Statement: (A) It is used for the synthesis of ATP: This is correct. The electromotive force generated by the electron transfer chain is indeed used to drive the synthesis of ATP through chemiosmosis in the mitochondria.
(B) It is not used for active transport processes: This statement is incorrect. The proton gradient created by the electron transfer chain, part of the electromotive force, is used for various active transport processes across the mitochondrial membrane.
(C) It includes a pH gradient component: This is correct. The creation of a proton gradient, which involves a difference in pH across the mitochondrial membrane, is a critical component of the electromotive force used in ATP synthesis.
(D) It does not include an electrical potential gradient component: This statement is incorrect. The proton gradient results in both a pH gradient and an electrical potential gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. Conclusion:
Thus, the correct statements that accurately describe the electromotive force in the electron transfer chain are (A) and (C). This force is central to the mitochondrial process of energy conversion from nutrients to ATP, coupling electron transfer with proton translocation and ATP synthesis.
Top Questions on Mass spectrometry
- The major product in the given reaction sequence is Q. The mass spectrum of Q shows
([M] = molecular ion peak)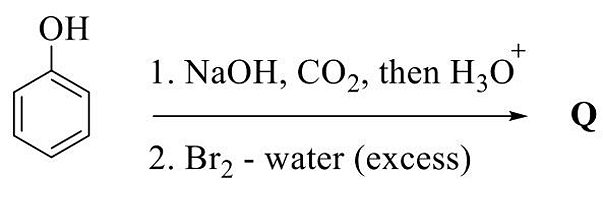
- GATE CY - 2024
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Mass spectrometry
- Which among the following characteristics of Laser light specifies the precise movement of all individual light waves together through time and space?
- AP PGECET - 2024
- Instrumentation Engineering
- Mass spectrometry
- Recombination of electron-hole produces ____ in LEDs.
- AP PGECET - 2024
- Instrumentation Engineering
- Mass spectrometry
- Magnetic sector analyzer is a part of
- AP PGECET - 2024
- Instrumentation Engineering
- Mass spectrometry
- Which ionization technique in mass spectrometry is most suitable for large biomolecules like proteins:
- GPAT - 2024
- Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Mass spectrometry
Questions Asked in GATE XL exam
- Imagine a population of diploid species in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The population has two alleles for a gene which are ‘a’ and ‘A’. The number of individuals with ‘aa’ genotype in this population is 1 in 10000. The frequency of the allele ‘A’ in the population is ............ (up to two decimal places)
- GATE XL - 2025
- Zoology
- The \( F_{121} \) value of a known microorganism with \( Z \) value of \( 11^\circ C \) is 2.4 min for 99.9999% inactivation. For a 12D inactivation of the said microorganism at \( 143^\circ C \), the \( F \) value (in min) is .......... {(rounded off to 3 decimal places)}
- GATE XL - 2025
- Food Technology
- In a typical grinding operation, 80% of the feed material passes through a sieve opening of 4.75 mm; whereas, 80% of the ground product passes through 0.5 mm opening. If the power required to grind 2 tonnes/h of the feed material is 3.8 kW, the work index of the material is ........ (rounded off to 2 decimal places)
- GATE XL - 2025
- Food Technology
- The true density and bulk density of wheat grains are 1280 kg/m\(^3\) and 740 kg/m\(^3\), respectively. The porosity of the grains is ......... (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
- GATE XL - 2025
- Food Technology
- An enzyme, which follows Michaelis-Menten equation, catalyzes the reaction A\(\rightarrow\)B. When enzyme and substrate concentrations are 15 nM and 10 \(\mu\)M, respectively, the reaction velocity is 5 \(\mu\)M s\(^{-1}\). If \(K_m\) for the substrate A is 5 \(\mu\)M, the kinetic efficiency of the enzyme will be ______ \(\times 10^6\) M\(^{-1}\) s\(^{-1}\) (in integer).
- GATE XL - 2025
- Zoology