Which of the reaction is suitable for concentrating ore by leaching process?
- \(2 Cu _2 S +3 O _2 \rightarrow 2 Cu _2 O +2 SO _2\)
- \(Fe _3 O _4+ CO \rightarrow 3 FeO + CO _2\)
- \(Al _2 O _3+2 NaOH +3 H _2 O \rightarrow 2 Na \left[ Al ( OH )_4\right]\)
- \(Al _2 O _3+6 Mg \rightarrow 6 MgO +4 Al\)
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The suitable reaction for concentrating ore by leaching process is:
\(Al _2 O _3+2 NaOH +3 H _2 O \rightarrow 2 Na \left[ Al ( OH )_4\right]\)
This is because the reaction involves the conversion of the metal oxide (in this case, aluminum oxide) into a water-soluble form (sodium aluminate), which can be easily separated from the impurities in the ore through leaching. Leaching involves dissolving the desired metal compound using a suitable solvent, in this case, sodium hydroxide solution. This process allows for the concentration of the ore by selectively dissolving the desired metal compound while leaving behind the impurities.
So, the correct option is (C).
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The system of linear equations
$x + y + z = 6$
$2x + 5y + az = 36$
$x + 2y + 3z = b$
has- JEE Main - 2026
- Matrices and Determinants
- The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with time period \(T\) is expressed as \[ x(t)=A\sin\omega t, \] where \(A\) is the amplitude of oscillation. If the maximum value of the potential energy of the oscillator is found at \[ t=\frac{T}{2\beta}, \] then the value of \(\beta\) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Waves and Oscillations
- A complex number 'z' satisfy both \(|z-6|=5\) & \(|z+2-6i|=5\) simultaneously. Find the value of \(z^3 + 3z^2 - 15z + 141\).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Algebra
In the given figure, the blocks $A$, $B$ and $C$ weigh $4\,\text{kg}$, $6\,\text{kg}$ and $8\,\text{kg}$ respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surfaces is $0.5$. The force $\vec{F}$ required to slide the block $C$ with constant speed is ___ N.
(Given: $g = 10\,\text{m s}^{-2}$)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational Mechanics
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational motion
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
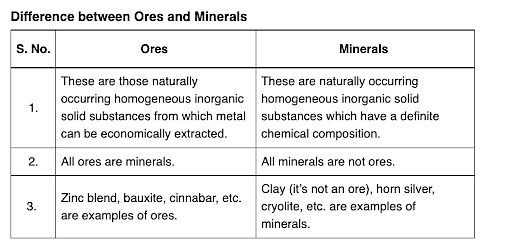
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal