What is an equilateral triangle?
Show Hint
- Whose three interior angles are equal
- Whose three walls are big and small
- Whose two sides are equal
- None of these
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Definition of Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal in length.
By the properties of triangles, if all sides are equal, then all angles are also equal.
Step 2: Use angle property
Each interior angle of an equilateral triangle is:
\[
\frac{180^\circ}{3} = 60^\circ
\]
So, not only are the three sides equal, but the three interior angles are also equal — each measuring \( 60^\circ \).
Step 3: Eliminate wrong options
- (B): "Walls" is irrelevant and vague in geometric context.
- (C): This describes an isosceles triangle, not equilateral.
- (D): Incorrect — there is a valid correct definition.
\[
\boxed{\text{Correct Answer: (A) Whose three interior angles are equal}}
\]
Top Questions on Classification of Triangles
- Number of Triangles in given figure:

- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Informatics Practices
- Classification of Triangles
- Name the types of following triangles:
(a) Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
(b) \(∆ABC\) with AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
(c) \(∆PQR\) such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(d) \( ∆DEF\) with m\(∠\) D = 90°
(e) \(∆XYZ\) with m \(∠\)Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
(f) \(∆LMN\) with m \(∠\)L = 30°, m \(∠\)M = 70° and m \(∠\)N = 80°.- CBSE Class VI
- Mathematics
- Classification of Triangles
- Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here. Can you make a triangle with:
(a) 3 matchsticks?
(b) 4 matchsticks?
(c) 5 matchsticks?
(d) 6 matchsticks? (Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case) If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
- CBSE Class VI
- Mathematics
- Classification of Triangles
- Name each of the following triangles in two different ways: (You may judge the nature of angle by observation)
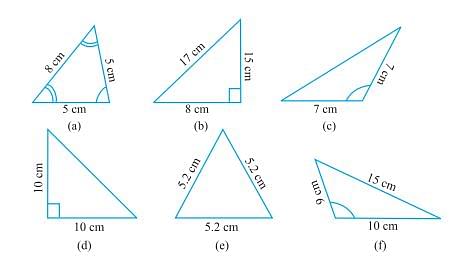
- CBSE Class VI
- Mathematics
- Classification of Triangles
- Match the following:
Measure of Triangle Types of Triangle (i) 3 sides of equal length (a) Scalene (ii) 2 sides of equal length (b) Isosceles right angle (iii) All sides are of different length (c) Obtuse angle (iv) 3 acute angles (d) Right angle (v) 1 right angle (e) Equilateral (vi) 1 obtuse angle (f) Acute angle (vii) 1 right angle with two sides of equal length (g) Isosceles - CBSE Class VI
- Mathematics
- Classification of Triangles
Questions Asked in UP Board X exam
- Colour origin from
- UP Board X - 2025
- Light and Colour
- How many national political parties are there in India?
- UP Board X - 2025
- Parties and the Party Systems in India
- Prime factorisation of 156 will be:
- UP Board X - 2025
- Number System
- (i) Food chain
(ii) Growth hormone in human.- UP Board X - 2025
- Food Chains and Energy Flow
- A lemon placed in a beaker full of water appears larger than its real size, when viewed sideways. The light phenomenon responsible is -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Refraction of Light