Two sides of a rhombus are along the lines, $x - y + 1 = 0$ and $7x - y - 5 = 0$. If its diagonals intersect at $(-1, -2)$, then which one of the following is a vertex of this rhombus?
- (-3 , -9)
- (-3 , -8)
- $\left( \frac{1}{3} , - \frac{8}{3} \right)$
- $\left( - \frac{10}{3} , - \frac{7}{3} \right)$
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation

Coordinates of $A \equiv (1, 2)$
$\therefore$ Slope of $AE = 2$
$\Rightarrow $ Slope of $BD = - \frac{1}{2}$ $\Rightarrow $
E of $BD$ is $\frac{y + 2 }{ x +1 } = - \frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow x + 2y + 5 = 0$
$\therefore$ Co-ordinates of $D = \left( \frac{1}{3} , \frac{-8}{3} \right)$
So, the correct option is (C): \(\left( \frac{1}{3} , - \frac{8}{3} \right)\)
Top Questions on Straight lines
- Rhombus vertices A(1,2), C(-3,-6). Line AD parallel to $7x-y=14$. Find $|\alpha+\beta+\gamma+\delta|$.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- Let the angles made with the positive $x$-axis by two straight lines drawn from the point $P(2,3)$ and meeting the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$ from the point $P$ be $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$. Then the value of $(\theta_1+\theta_2)$ is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- The equation of a straight line is given by \( y = 3x + 4 \). What is the slope of the line?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Straight lines
A straight line is a line having the shortest distance between two points.
A straight line can be represented as an equation in various forms, as show in the image below:
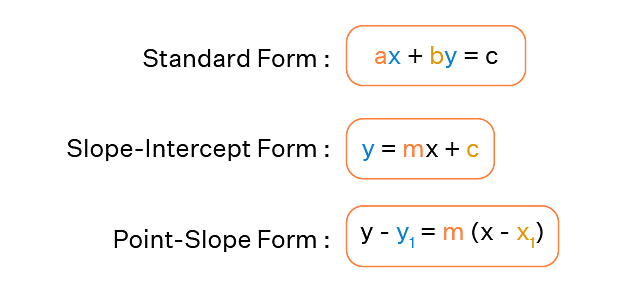
The following are the many forms of the equation of the line that are presented in straight line-
1. Slope – Point Form
Assume P0(x0, y0) is a fixed point on a non-vertical line L with m as its slope. If P (x, y) is an arbitrary point on L, then the point (x, y) lies on the line with slope m through the fixed point (x0, y0) if and only if its coordinates fulfil the equation below.
y – y0 = m (x – x0)
2. Two – Point Form
Let's look at the line. L crosses between two places. P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) are general points on L, while P (x, y) is a general point on L. As a result, the three points P1, P2, and P are collinear, and it becomes
The slope of P2P = The slope of P1P2 , i.e.
\(\frac{y-y_1}{x-x_1} = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
Hence, the equation becomes:
y - y1 =\( \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} (x-x1)\)
3. Slope-Intercept Form
Assume that a line L with slope m intersects the y-axis at a distance c from the origin, and that the distance c is referred to as the line L's y-intercept. As a result, the coordinates of the spot on the y-axis where the line intersects are (0, c). As a result, the slope of the line L is m, and it passes through a fixed point (0, c). The equation of the line L thus obtained from the slope – point form is given by
y – c =m( x - 0 )
As a result, the point (x, y) on the line with slope m and y-intercept c lies on the line, if and only if
y = m x +c