The value of b > 3 for which \(12∫_3^b \frac{1}{(x^2-1)(x^2-4)}dx=log_e(\frac{40}{40}) \) is equal to.
Correct Answer: 6
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is: 6
\(l=∫_3^b \frac{1}{(x^2-1)(x^2-4)}dx=\frac{1}{3}(\frac{1}{x^2-4}-\frac{1}{x^2-1})dx\)
\(=ln((\frac{b-2}{b+2})\frac{(b+1)^2}{b-1}^2)-(In\,\frac{4}{5})\)
After simplification ,
\(\frac{49}{40}=\frac{(b-2)}{(b+2)}\frac{(b+1)^2}{(b-1)^2}.\frac{5}{4}\)
⇒ b = 6
Top Questions on types of differential equations
- Let the system of equations \(x+2y+3z = 5\), \(2x+3y+z = 9\), \(4x+3y+λz = μ\) have an infinite number of solutions. Then \(λ + 2μ\) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \) are the slopes of the direct common tangents drawn to the circles \[ x^2 + y^2 - 2x - 8y + 8 = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad x^2 + y^2 - 8x + 15 = 0 \] then \( m_1 + m_2 \) is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If \( (2,3) \) is the focus and \( x - y + 3 = 0 \) is the directrix of a parabola, then the equation of the tangent drawn at the vertex of the parabola is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If the focus of an ellipse is \((-1,-1)\), equation of its directrix corresponding to this focus is \(x + y + 1 = 0\) and its eccentricity is \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\), then the length of its major axis is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- The equation of the common tangent to the parabola \(y^2 = 8x\) and the circle \(x^2 + y^2 = 2\) is \(ax + by + 2 = 0\). If \(-\frac{a}{b}>0\), then \(3a^2 + 2b + 1 =\)
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
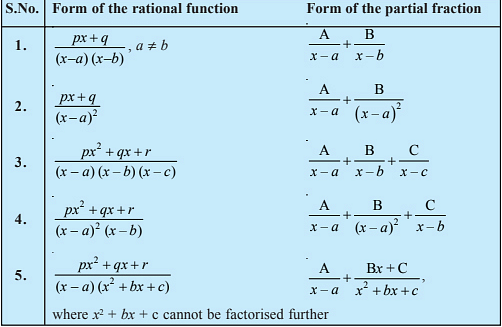
For examples,
