The refracting angle of prism is A and refractive index of material of prism is $\cot \frac{A}{2}$ The angle of minimum deviation is
- $180^\circ -3 A$
- $180^\circ +2 A$
- $90^\circ - A$
- $180^\circ -2 A$
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
For a prism, the relation between the refracting angle \( A \), the refractive index \( n \), and the angle of minimum deviation \( \delta \) is given by: \[ n = \cot \frac{A}{2} \] The angle of minimum deviation \( \delta \) is related to the refracting angle \( A \) by the equation: \[ \delta = 180^\circ - 2A \] Thus, the angle of minimum deviation is \( 180^\circ - 2A \).
Approach Solution -2
$\Rightarrow \cot \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)=\frac{\sin \left(\frac{A+d_{m}}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\cos \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}=\frac{\sin \left(\frac{A+d_{m}}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}$
$\Rightarrow \sin \left(90-\frac{A}{2}\right)=\sin \left(\frac{A+d_{m}}{2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow 90-\frac{A}{2}=\frac{A+d_{m}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 180-2 A=d_{m}$
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
Questions Asked in KCET exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
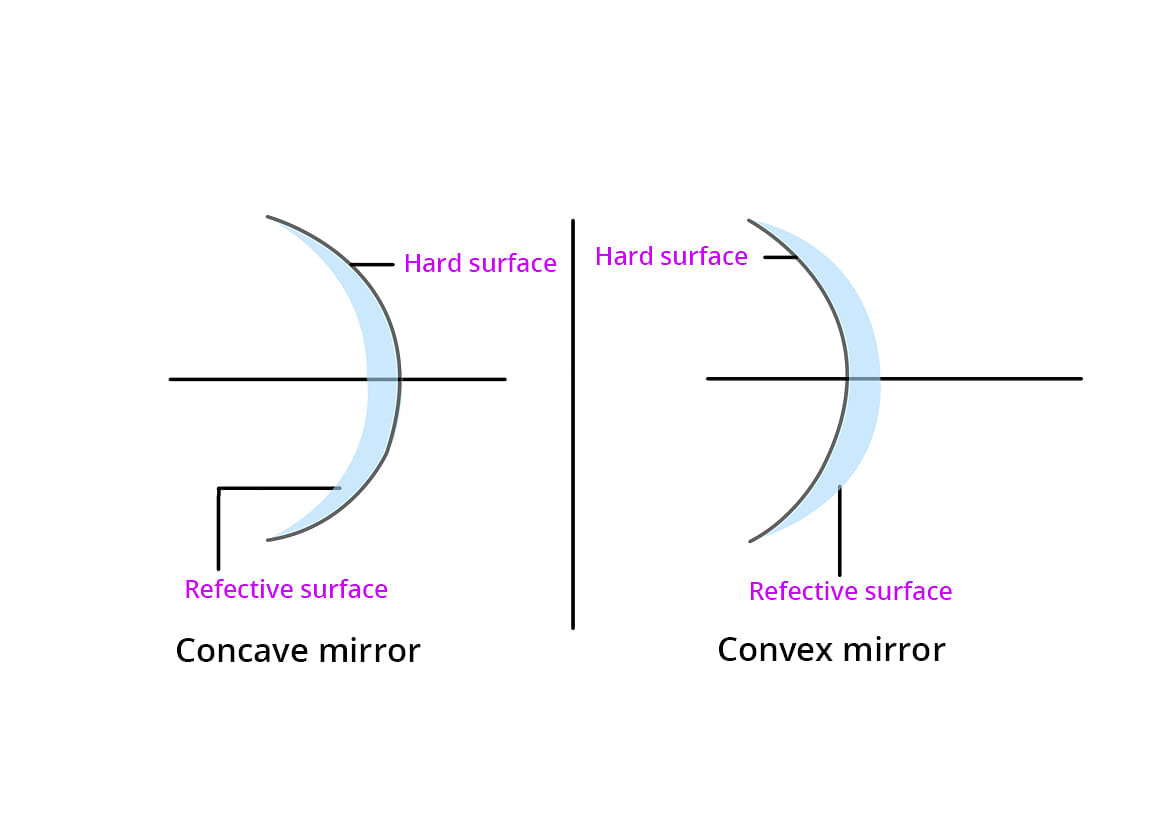
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.