The correct option(s) of the reagents required for the following reaction is/are
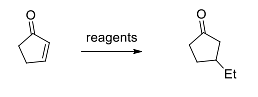
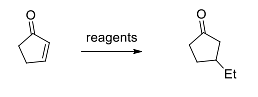
- (i) Et3B, O2 (cat), THF; (ii) H2O
- (i) Et2CuLi, Me3SiCl; (ii) H3O+
- (i) EtMgBr, Et2O; (ii) H2O
- (i) "BuLi, THF; (ii) EtI
The Correct Option is A, B
Solution and Explanation
The given reaction involves the conversion of a carbonyl compound into its ethyl-substituted derivative. To identify the correct reagents, let's examine the function of each given option:
- The correct answer is (i) Et3B, O2 (cat), THF; (ii) H2O and (i) Et2CuLi, Me3SiCl; (ii) H3O+. Here's an explanation for each:
- Et3B, O2 (cat), THF; (ii) H2O: This reagent combination utilizes trialkylborane and catalytic oxygen in the presence of THF. The role of the trialkylborane is to participate in hydroboration, introducing an ethyl group into the molecule. Subsequent water addition facilitates the rearrangement to form the desired ethyl ketone.
- Et2CuLi, Me3SiCl; (ii) H3O+: This mixture involves a Gilman reagent (Et2CuLi) that is capable of adding an ethyl group to the carbonyl. The Me3SiCl is used to protect the resulting intermediate, and the acidic workup (H3O+) regenerates the ketone.
- The incorrect options:
- (i) EtMgBr, Et2O; (ii) H2O: The Grignard reagent (EtMgBr) adds an ethyl group to carbonyls but leads to alcohol formation, not the desired ketone.
- (i) "BuLi, THF; (ii) EtI: n-Butyllithium is a strong base and can lead to deprotonation rather than substitution, and ethyl iodide in the presence of a strong base can lead to side reactions, not delivering the desired product.
Hence, options (i) Et3B, O2 (cat), THF; (ii) H2O and (i) Et2CuLi, Me3SiCl; (ii) H3O+ are appropriate for this transformation of adding an ethyl group to the carbonyl compound to form an ethyl ketone.
Top Questions on Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
- The reaction represented by \( A \rightarrow B \) follows first-order kinetics. At a given temperature, 20% of the reaction is completed in 223 s. The time taken to complete 50% of the reaction at the same temperature is _________ s (rounded off to the nearest integer).
- GATE MT - 2025
- Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy
- Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
- Consider the following reactions and their standard Gibbs free energies (in J): \[ {Fe(s)} + \frac{1}{2} {O}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons {FeO(s)} \quad \Delta G^\circ = -264900 + 65T \] \[ 2 {H}_2(g) + {O}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 {H}_2{O(g)} \quad \Delta G^\circ = -492900 + 109T \] Assuming Fe and FeO to be pure and no solubility of gases in the solids, the value of \( \frac{p_{H_2O}}{p_{H_2}} \) required to reduce solid FeO to solid Fe at 1000 K is _________ (rounded off to two decimal places). Given: Ideal gas constant \( R = 8.314 \, {J mol}^{-1} {K}^{-1} \).
- GATE MT - 2025
- Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy
- Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
- Molten steel at 1900 K having dissolved hydrogen needs to be vacuum degassed. The equilibrium partial pressure of hydrogen to be maintained to achieve 1 ppm (mass basis) of dissolved hydrogen is ......... Torr (rounded off to two decimal places). Given: For the hydrogen dissolution reaction in molten steel \( \left( \frac{1}{2} {H}_2(g) = [{H}] \right) \), the equilibrium constant (expressed in terms of ppm of dissolved H) is: \[ \log_{10} K_{eq} = \frac{1900}{T} + 2.4 \] 1 atm = 760 Torr.
- GATE MT - 2025
- Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy
- Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
- Consider the gas phase reaction: \[ CO + \frac{1}{2} O_2 \rightleftharpoons CO_2 \] At equilibrium for a particular temperature, the partial pressures of \( CO \), \( O_2 \), and \( CO_2 \) are found to be \( 10^{-6} \, {atm} \), \( 10^{-6} \, {atm} \), and \( 16 \, {atm} \), respectively. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is ......... \( \times 10^{10} \) (rounded off to one decimal place).
- GATE MT - 2025
- Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy
- Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
- In the Claisen-Schmidt reaction to prepare dibenzalacetone from 5.3 g benzaldehyde, a total of 3.51 g of product was obtained. The percentage yield in this reaction was _____.
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Reaction Mechanisms & Synthesis
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- Among the following, the correct condition(s) for spontaneity is(are)
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas starting from state A, goes through B and C to state D, as shown in the figure. Total change in entropy (in J K\(^{-1}\)) during this process is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
The number of chiral carbon centers in the following molecule is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
- Consider the following matrices A and B.
\[ A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 7 \\ 0 & 0 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B = \begin{pmatrix} 10 & 11 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 12 & 13 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 15 & 16 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 17 & 18 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
If \( C = AB \), the sum of the diagonal elements of \( C \) is ..............
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
A tube fitted with a semipermeable membrane is dipped into 0.001 M NaCl solution at 300 K as shown in the figure. Assume density of the solvent and solution are the same. At equilibrium, the height of the liquid column \( h \) (in cm) is .........

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry