Sound waves in air are always longitudinal because,
- air is a mixture of several gases
- density of air is very small
- of the inherent characteristics of sound waves in air
- air does not have a modulus of rigidity
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on doppler effect
- A passenger is sitting in a fast moving train. The engine of the train blows a whistle of frequency N. If the apparent frequency of sound heard by the passengers is \( N' \), then:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Physics
- doppler effect
- When both the source of sound and observer approach each other with a speed equal to 10% of the speed of sound, then the percentage change in frequency heard by the observer is nearly
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A source (S) of sound has frequency\( 240 Hz\). When the observer (O) and the source move towards each other at a speed \(v\) with respect to the ground (as shown in Case 1 in the figure), the observer measures the frequency of the sound to be \(288 Hz\). However, when the observer and the source move away from each other at the same speed v with respect to the ground (as shown in Case 2 in the figure), the observer measures the frequency of sound to be \(n\) Hz. The value of \(n\) is _____.
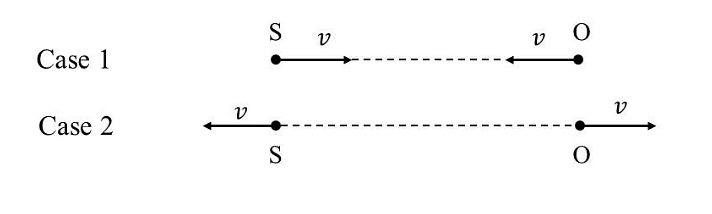
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A galaxy is moving away from the Earth so that a spectral line at 6000 Å is observed at 6300 Å. Then the speed of the galaxy with respect to the Earth is
- KCET - 2024
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A train is moving with a speed of \(10 m/s\) towards a platform and blows a horn with frequency \(400 Hz\). Find the frequency heard by a passenger standing on the platform. Take speed of sound = \(310 m/s\).
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- doppler effect
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is a phenomenon caused by a moving wave source that causes an apparent upward shift in frequency for observers who are approaching the source and a visible downward change in frequency for observers who are retreating from the source. It's crucial to note that the impact isn't caused by a change in the source's frequency.

The Doppler effect may be seen in any wave type, including water waves, sound waves, and light waves. We are most familiar with the Doppler effect because of our encounters with sound waves