Match List I with List II.
List-I List-II A. Benzene sulphonyl chloride I. Test for primary amines B. Hoffmann bromamide reaction II. Anti Saytzeff C. Carbylamine reaction III. Hinsberg reagent D. Hoffmann orientation IV. Known reaction of Isocyamates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List I with List II.
| List-I | List-II |
| A. Benzene sulphonyl chloride | I. Test for primary amines |
| B. Hoffmann bromamide reaction | II. Anti Saytzeff |
| C. Carbylamine reaction | III. Hinsberg reagent |
| D. Hoffmann orientation | IV. Known reaction of Isocyamates |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
- A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-II
- A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
- A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
To solve this matching question, we need to associate each item from List-I with the correct option from List-II based on their known chemical reactions and applications. Let's go through each option step by step:
- Benzene sulphonyl chloride is known as the Hinsberg reagent. It is used for the test of amines, particularly to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. Therefore, A matches with III.
- The Hoffmann bromamide reaction is a well-known reaction that converts an amide into an amine with the loss of a carbon atom. This reaction also involves the formation of an isocyanate intermediate. Hence, B matches with IV.
- The Carbylamine reaction is a test for primary amines. It involves the formation of an isocyanate intermediate and produces a foul-smelling compound when primary amines are treated with chloroform and an alcoholic base. So, C matches with I.
- Hoffmann orientation leads to anti-Saytzeff orientation in elimination reactions. This means that the less substituted alkene (less stable) is formed in preference to the more substituted one. Thus, D matches with II.
Based on the above associations, the correct matching is:
- A - III
- B - IV
- C - I
- D - II
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Top Questions on Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their acidic strength: (A) 3-nitrophenol
(B) 3,5-Dinitrophenol
(C) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
(D) Phenol
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Rate of a Chemical Reaction
The speed at which a chemical reaction takes place is called the rate of reaction. The rate of reaction depends on various factors like concentration of the reactants, temperature, etc. The relation between the rate of reaction and the concentration of reacting species is represented by the equation \( r = k[A]^x[B]^y \), where \( x \) and \( y \) are the order of the reaction with respect to the reactants A and B, respectively. The overall order of the reaction is \( x + y \). The rate of reaction can also be increased by the use of a catalyst which provides an alternate pathway of lower activation energy. It increases the rate of forward and backward reactions to an equal extent. It does not alter the Gibbs energy of the reaction.
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Which among the following is a false statement?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- In a reaction, \( 3A \rightarrow \text{Products} \), the concentration of \( A \) decreases from 0.6 mol L\(^{-1}\) to 0.3 mol L\(^{-1}\) in 20 minutes. What is the rate of the reaction during this interval?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Which factor in the Arrhenius equation corresponds to the fraction of molecules having kinetic energy greater than activation energy?
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Rate of a Chemical Reaction
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Let $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}-\hat{j}-\hat{k}$, $\vec{b}=\hat{i}+3\hat{j}-\hat{k}$ and $\vec{c}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}$. Let $\vec{v}$ be the vector in the plane of $\vec{a}$ and $\vec{b}$, such that the length of its projection on the vector $\vec{c}$ is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{14}}$. Then $|\vec{v}|$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Vector Algebra
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
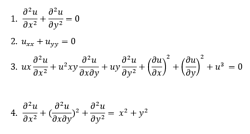
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
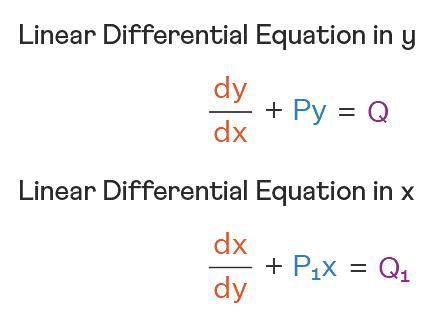
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations