Let S={z=x+iy:|z–1+i|≥|z|,|z|<2,|z+i|=|z–1|}.
Then the set of all values of x, for which w = 2x + iy ∈ S for some y ∈ R is
Then the set of all values of x, for which w = 2x + iy ∈ S for some y ∈ R is
(-\(\sqrt2\),\(\frac{1}{2\sqrt2}\))
(-\(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\),\(\frac{1}{4}\))
(-\(\sqrt2\),\(\frac{1}{2}\))
(\(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\),\(\frac{1}{2\sqrt2}\))
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
To solve this problem, we need to determine the set of all values of \( x \) for which \( w = 2x + iy \in S \) for some \( y \in \mathbb{R} \), where \( S = \{ z = x + iy : |z - 1 + i| \geq |z|, |z| < 2, |z + i| = |z - 1| \} \).
- Let's analyze the given conditions for \( z = x + iy \).
- The first condition, \( |z - 1 + i| \geq |z| \), represents the region outside or on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the point \( (1, -1) \) and the origin. Simplifying this, it gives us:
- \( |(x - 1) + (y + 1)i| \geq |x + yi| \) simplifies to \( (x - 1)^2 + (y + 1)^2 \geq x^2 + y^2 \).
- This expands to \( x^2 - 2x + 1 + y^2 + 2y + 1 \geq x^2 + y^2 \).
- After canceling terms, we get \( -2x + 2y + 2 \geq 0 \) or \( x \leq y + 1 \).
- The second condition, \( |z| < 2 \), represents the region inside the circle centered at the origin with radius 2.
- The third condition, \( |z + i| = |z - 1| \), is the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points \(-i\) and \(1\). Simplifying this:
- \( |x + (y + 1)i| = |x - 1 + yi| \).
- Squaring both sides gives \( x^2 + (y+1)^2 = (x-1)^2 + y^2 \).
- This simplifies to \( x^2 + y^2 + 2y + 1 = x^2 - 2x + 1 + y^2 \), leading to \( 2y = -2x \), or \( y = -x \).
- Combine these results:
- The condition \( y = -x \) and \( x \leq y + 1 \) means \( x \leq -x + 1 \), or \( 2x \leq 1 \). Thus, \( x \leq \frac{1}{2} \).
- Additionally, since \( |z| < 2 \), \( \sqrt{x^2 + y^2} = \sqrt{x^2 + (-x)^2} = \sqrt{2x^2} < 2 \), or \( x^2 < 2 \), giving \( |x| < \sqrt{2} \).
- Next, find the range of \( w = 2x + iy \). Substituting \( y = -x \) into \( w \), we have:
- \( w = 2x + i(-x) = 2x - ix \).
- This implies \( Re(w) = 2x \).
- Using \( x \leq \frac{1}{2} \) and \( |x| < \sqrt{2} \), we find the possible range for \( 2x: -2\sqrt{2} < 2x < 1 \).
- Thus, \( -\sqrt{2} < x < \frac{1}{2} \).
- Finally, comparing these intervals with the given options, we determine the correct range of \( x \).
The correct answer is: \((- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \frac{1}{4})\).
Approach Solution -2
S:{z=x+iy:|z–1+i|≥|z|,|z|<2,|z–i|=|z–1|}|z–1+i|≥|z|
|z| < 2
|z–i|=|z–1|
∵ w∈S and w=2x+iy
2x<\(\frac{1}{2}\) ∴x<\(\frac{1}{4}\)
(2x)2+(−2x)2<4
4x2+4x2<4
x2<\(\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒x∈(−\(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\),\(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\))
∴x∈(−\(\frac{1}{2}\),\(\frac{1}{4}\))
So, the correct option is (B).
Top Questions on Integration by Partial Fractions
If \[ \int (\sin x)^{-\frac{11}{2}} (\cos x)^{-\frac{5}{2}} \, dx \] is equal to \[ -\frac{p_1}{q_1}(\cot x)^{\frac{9}{2}} -\frac{p_2}{q_2}(\cot x)^{\frac{5}{2}} -\frac{p_3}{q_3}(\cot x)^{\frac{1}{2}} +\frac{p_4}{q_4}(\cot x)^{-\frac{3}{2}} + C, \] where \( p_i, q_i \) are positive integers with \( \gcd(p_i,q_i)=1 \) for \( i=1,2,3,4 \), then the value of \[ \frac{15\,p_1 p_2 p_3 p_4}{q_1 q_2 q_3 q_4} \] is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let for \( f(x) = 7\tan^8 x + 7\tan^6 x - 3\tan^4 x - 3\tan^2 x \), \( I_1 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} f(x)dx \) and \( I_2 = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{4}} x f(x)dx \). Then \( 7I_1 + 12I_2 \) is equal to:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Let {an}n=0∞ be a sequence such that a0=a1=0 and an+2=3an+1−2an+1,∀ n≥0. Then a25a23−2a25a22−2a23a24+4a22a24 is equal to
- JEE Main - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- Find the value of \( \frac{5}{6} + \frac{3}{4} \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
- If ∫ (2x + 3)/((x - 1)(x^2 + 1)) dx = log_x {(x - 1)^(5/2)(x^2 + 1)^a} - (1/2) tan^(-1)x + C, then the value of a is:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Integration by Partial Fractions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
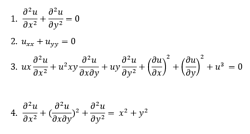
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
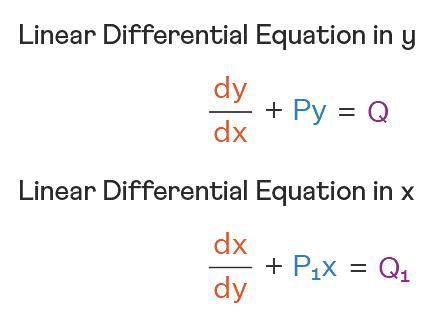
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations